This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Making plant-based meat alternatives more palatable with protein microgels
One of the biggest obstacles to the uptake of plant-based alternatives to meat is their very dry and astringent feel when they are eaten.
Scientists, led by Professor Anwesha Sarkar at the University of Leeds, are revolutionizing the sensation of plant proteins, transforming them from a substance that can be experienced as gloopy and dry to one that is juicy and fat like.
And the only substance they are adding to the plant proteins is water.
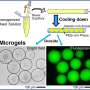
Plant protein microgels
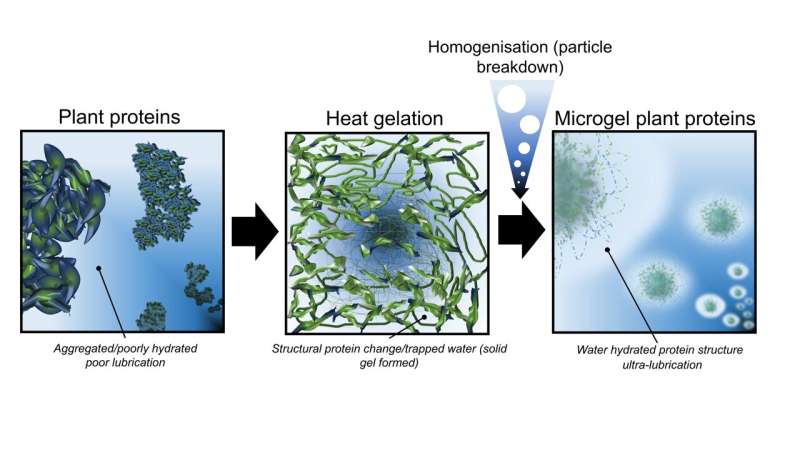
To bring about this change, the scientists created plant protein microgels, through a process called microgeletion.
Plant proteins—which start off as dry with a rough texture—are placed in water and subjected to heating. This alters the structure of the protein molecules which come together to form an interconnected network or gel which traps water around the plant proteins.
The gel is then homogenized, which breaks the protein network into a microgel made up of tiny particles that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Under pressure, as they would be when they are being eaten, the microgels ooze water, creating a lubricity akin to that of single cream.
Professor Sarkar said, "What we have done is converted the dry plant protein into a hydrated one, using the plant protein to form a spider-like web that holds the water around the plant protein."
"This gives the much-needed hydration and juicy feel in the mouth.
"Plant-based protein microgels can be created without having to use any added chemicals or agents using a technique that is widely available and currently used in the food industry. The key ingredient is water."
Revitalizing consumer interest
The research team, who have published their findings in the journal Nature Communications, say the dryness of plant proteins has been a "key bottle neck for consumer acceptability."
With the breakthrough, the research team hope consumer interest in plant-based proteins will be revitalized, encouraging people to reduce their reliance on animal products for protein intake, a necessary step if global climate change targets are to be met.
More than half of the 18 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents produced each year from food production comes from rearing and processing animal products.
The researchers say the protein microgels "offer a unique platform to design the next generation of healthy, palatable and sustainable foods."
Eureka moment
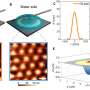
Throughout the investigation, the team had mathematically modeled the behavior of plant protein microgels and were confident their approach would work.
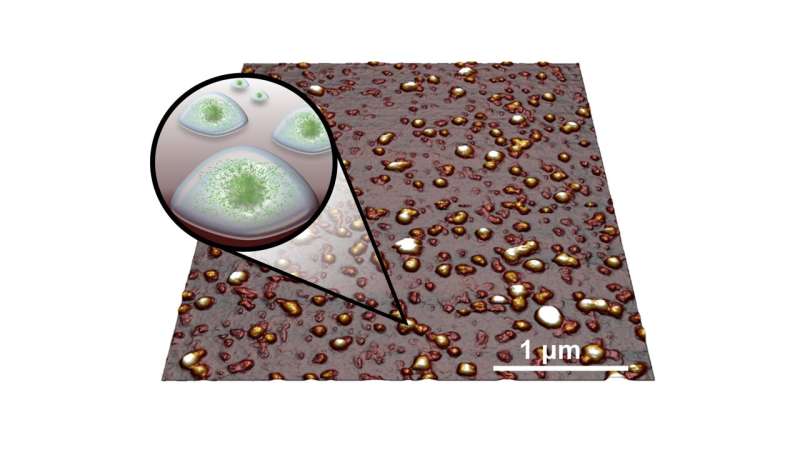
But the proof came in visualizations produced in the atomic force microscopy suite in the Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences at Leeds. Atomic force microscopy involves a tiny probe scanning the surface of a molecule to get a picture of its shape.
What those images revealed amounted to a proof of concept.
Professor Sarkar added, "Seeing the images from the atomic force microscope was a such as exciting moment for us. The visualizations revealed that the protein microgels were pretty much spherical and not aggregating or clumping together. We could see individually spaced plant protein microgels.
"Our theoretical studies had said this is what would happen but there is nothing quite like seeing it for real."
Dr. Mel Holmes, Associate Professor in the School of Food Science and Nutrition at Leeds and one of the authors of the paper, said, "This study reveals the ingenuity and depth of science involved in modern food technology, from the chemistry of proteins, the way food is sensed in the mouth to an understanding of tribology—the friction between materials and sensory cells in the mouth."
"Tackling the big questions in food science requires interdisciplinary science."
Wider spin offs of plant protein microgels
Given the lubricity of the microgels, akin to that of a single cream, means they could be adapted for other uses in the food processing industry, such as replacing fat that has been removed from a foodstuff to develop healthier options.
Ben Kew, doctoral student in the School of Food Science and Nutrition at Leeds and lead researcher in the project, said, "This is quite a remarkable finding. It is striking that without adding a drop of fat, the microgels resembles the lubricity of a 20% fat emulsion, which we are the first to report."
"Our experimental data supported by theoretical analyses also mean we could begin to use these plant protein microgels in foods where fat has to be removed to reformulate into healthier next generation plant protein food options."
More information: Ben Kew et al, Transforming sustainable plant proteins into high performance lubricating microgels, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40414-7
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Leeds