This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Electrocatalytic CO2 reduction by enrichment of reactants and intermediates

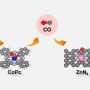
The use of electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction for the production of high value-added multicarbon fuels (ethylene, ethanol, acetic acid, n-propanol) is hampered by low selectivity and conversion rates, and its performance has not yet met the requirements for industrial production.
An important constraint to the development of this technology is the low solubility and diffusion coefficient of carbon dioxide in the aqueous phase, and the ease with which carbon dioxide reacts with hydroxide in aqueous solution to form carbonates. This results in low concentrations of carbon dioxide and intermediates near the catalytic site, severely limiting the conversion of carbon dioxide to multicarbon products.
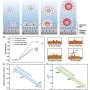
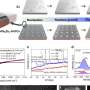
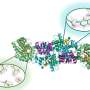
Existing studies have shown that the enrichment of CO2 molecules and carbon-based intermediates in the vicinity of the catalytic site can increase the percentage of activated molecules per unit volume and enhance the effective collision between molecules, which can accelerate the reaction rate and improve the selectivity of the conversion of CO2 into multicarbon products.
A research team led by Prof. Gao Minrui from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have now published a review paper entitled "Enrichment of reactants and intermediates for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction" in Chemical Society Reviews.
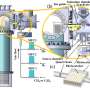
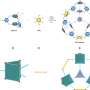
The researchers systematically summarized the enrichment strategies in the CO2 reduction reaction in terms of the structure and properties of CO2 molecules, catalyst design, catalyst reconfiguration, local microenvironmental regulation, electrolyte regulation and electrolysis device optimization, and they analyzed in-depth the mechanisms of reactants and intermediates enrichment in the different strategies from the macroscopic to the microscopic level. Finally, they predicted the challenges of the enrichment effect in the promotion of CO2 reduction as well as its future development.
More information: Peng-Peng Yang et al, Enrichment of reactants and intermediates for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction, Chemical Society Reviews (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D2CS00849A
Journal information: Chemical Society Reviews
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences