This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New superconductors can be built atom by atom, researchers show
The future of electronics will be based on novel kinds of materials. Sometimes, however, the naturally occurring topology of atoms makes it difficult for new physical effects to be created. To tackle this problem, researchers at the University of Zurich have now successfully designed superconductors one atom at a time, creating new states of matter.
What will the computer of the future look like? How will it work? The search for answers to these questions is a major driver of basic physical research. There are several possible scenarios, ranging from the further development of classical electronics to neuromorphic computing and quantum computers.
The common element in all these approaches is that they are based on novel physical effects, some of which have so far only been predicted in theory. Researchers go to great lengths and use state-of-the-art equipment in their quest for new quantum materials that will enable them to create such effects. But what if there are no suitable materials that occur naturally?
Novel approach to superconductivity
In a recent study published in Nature Physics, the research group of UZH Professor Titus Neupert, working closely together with physicists at the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics in Halle (Germany), presented a possible solution.
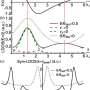
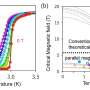
The researchers made the required materials themselves—one atom at a time. They are focusing on novel types of superconductors, which are particularly interesting because they offer zero electrical resistance at low temperatures. Sometimes referred to as "ideal diamagnets," superconductors are used in many quantum computers due to their extraordinary interactions with magnetic fields. Theoretical physicists have spent years researching and predicting various superconducting states. "However, only a small number have so far been conclusively demonstrated in materials," says Professor Neupert.
Two new types of superconductivity
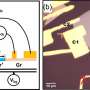
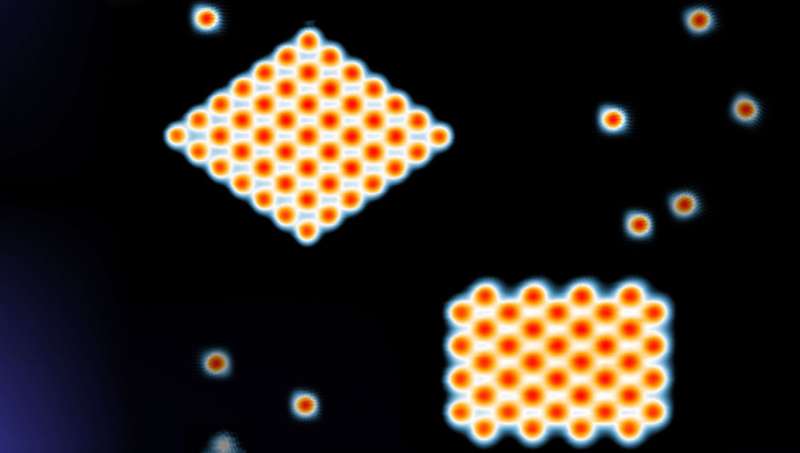
In their collaboration, the UZH researchers predicted how the atoms should be arranged to create a new superconductive phase, and the team in Germany then conducted experiments to implement the relevant topology.
Using a scanning tunneling microscope, they moved and deposited the atoms in the right place with atomic precision. The same method was also used to measure the system's magnetic and superconductive properties. By depositing chromium atoms on the surface of superconducting niobium, the researchers were able to create two new types of superconductivity. Similar methods had previously been used to manipulate metal atoms and molecules, but until now it has never been possible to make two-dimensional superconductors with this approach.
The results not only confirm the physicists' theoretical predictions, but also give them reason to speculate about what other new states of matter might be created in this way, and how they could be used in the quantum computers of the future.
More information: Martina O. Soldini et al, Two-dimensional Shiba lattices as a possible platform for crystalline topological superconductivity, Nature Physics (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-02104-5
Journal information: Nature Physics
Provided by University of Zurich