This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers construct non-interpenetrated 3D covalent organic framework for Au ions capture
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) can be an ideal platform for detecting or extracting metal ions due to their different functional building units and large surface area.
However, most 3D COFs have interpenetration because of the existence of non-covalent interactions between the adjacent nets, which results in decreased surface areas and porosities and thus limits their applications in catalysis and molecular/gas adsorption.
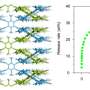
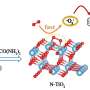
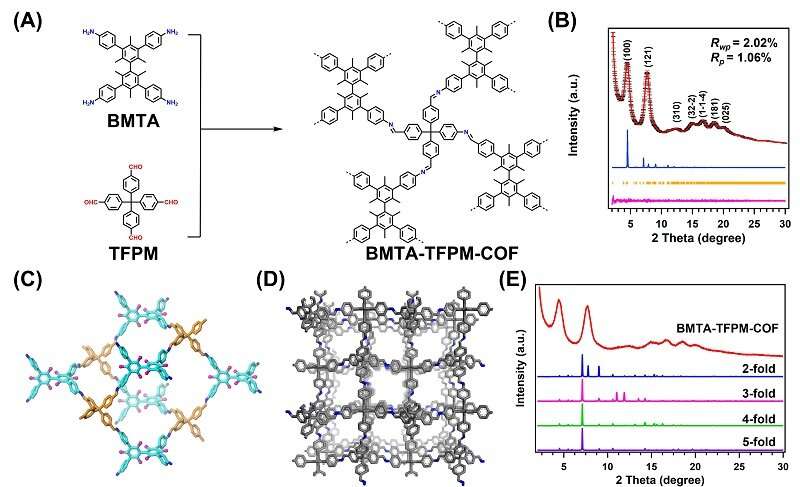
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Zeng Gaofeng and Assoc. Prof. Xu Qing from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has constructed a novel non-interpenetration 3D COF for Au ions capture by imine bonds in the frameworks. The high surface area and abundant cavities provided high Au3+ capacity (570.18 mg g-1), selectivity (99.5%) and efficiency (68.3% adsorption of maximum capacity in five mins).
The study was published in Advanced Functional Materials on April 23.
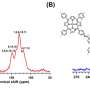
The synthesized BMTA-TFPM-COF displayed good crystallinity with dia topology and a high Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area of 1,924 m2 g-1. Importantly, the open cavities and exposed C=N bonds from non-fold interpenetration contributed to high capacity, selectivity and stability of Au3+ uptake.
The experiments showed the mechanism of Au capture. The protonated C=N bonds due to the influence of the HAuCl4 and the protonated nitrogenous groups could adsorb AuCl4- and reduce Au(III) to Au(I) and Au(0) in acidic solution. Thus, the BMTA-TFPM-COF with abundant exposed C=N bonds could promote the conversion from Au(III) to Au(I) and Au(0) through the protonated C=N bonds, which further verified that the C=N bonds could participate in the reduction of Au(III).
This study provides new insights into the development of 3D COFs for Au3+ capture.
More information: Minghao Liu et al, Non‐Interpenetrated 3D Covalent Organic Framework with Dia Topology for Au Ions Capture, Advanced Functional Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202302637
Journal information: Advanced Functional Materials
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences