This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study shows dramatic insect decline is also occurring in forests
The number of insects has been declining for years. This has already been well documented for agricultural areas. In forests, however, temporal trends are mostly studied for insect species that are considered pests.
Now, a research team led by the Technical University Darmstadt have studied the trends of very many insect species in German forests. Contrary to what the researchers had suspected, the results showed that the majority of the studied species are declining. The results have been published in Communications Biology.
Forests in Central Europe have recently come to the public's attention due to their importance for climate mitigation and due to the omnipresent forest damage as a result of hot and dry summers. In addition to humans, many animal species depend on forest ecosystems, most of which are insects.
Insects are often considered only as pests in the forest, as is shown, for example, by reports on bark beetles or cockchafers. While temporal changes in populations of potential insect pests are well studied, little is known about the status and trend of the many other fascinating insect species in forests.
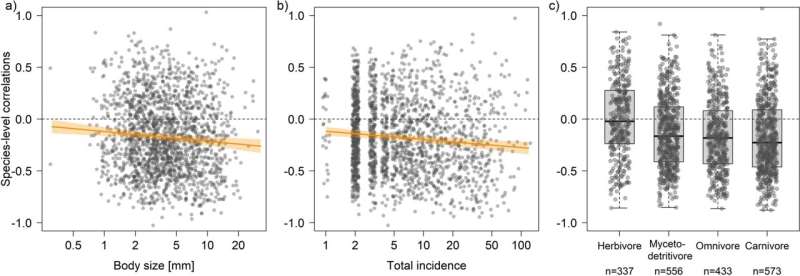
A new study led by researchers from the Technical Universities of Darmstadt and Munich in collaboration with other researchers now shows how the populations of 1,805 insect species have developed in German forests from 2008 to 2017. To the researchers' surprise, the number of individuals has declined over time for the majority of the evaluated species.
This is particularly surprising when compared to agricultural land, where the type of land use has changed over time and intensified, for example due to more effective pesticides, the removal of edge structures, or increased cultivation of corn. Disturbances of this type do not play a role in forests.
Nevertheless, a clear decline in forest species was demonstrated, with larger and more abundant species declining particularly. While slightly more species increased than decreased in herbivorous insects, significantly more species decreased in all other feeding types such as predators or deadwood decomposers.
The new study was conducted as part of the "Biodiversity Exploratories," an interdisciplinary infrastructure priority program supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) since 2006, in three regions: the Hainich National Park, the UNESCO Biosphere Reserve Schorfheide-Chorin and the UNESCO Biosphere Reserve Swabian Alb.
The decline was greater in forests with a high proportion of conifers, such as spruce and pine, which are naturally rare in the study areas but have been planted in the past. In contrast, losses of insects were lower in native beech forests. Furthermore, in unmanaged protected forests, the declines were less severe than in intensively managed forests.
With this to date most comprehensive study on insect decline in Central European forests, the authors show that insects are not only declining in agricultural landscapes—as previously demonstrated—but also in forests, which cover almost a third of the land area in Germany.
"More than 60 percent of the studied insect species have been declining," says the lead author of the study, Dr. Michael Staab from the Ecological Networks Groups of the Department of Biology at the Technical University Darmstadt. "This will very likely have an impact on all organisms in our forests as food webs may be altered." In light of climate change, future research is needed to unravel how increasing drought and the resulting changes in native forests will affect insect population trends.
Professor Nico Blüthgen, head of the Ecological Networks Group, adds, "Our forests are undergoing drastic changes due to the climate crisis. We are currently trying to understand how this affects insect populations." The results of the study suggest that targeted management, including promoting a more natural tree species composition and reduced tree harvest, can help mitigating insect decline in our forests.
More information: Michael Staab et al, Insect decline in forests depends on species' traits and may be mitigated by management, Communications Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-04690-9
Journal information: Communications Biology
Provided by Technische Universitat Darmstadt