This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Origin and effect of surface oxygen-containing species on electrochemical carbon/oxygen reduction reactions
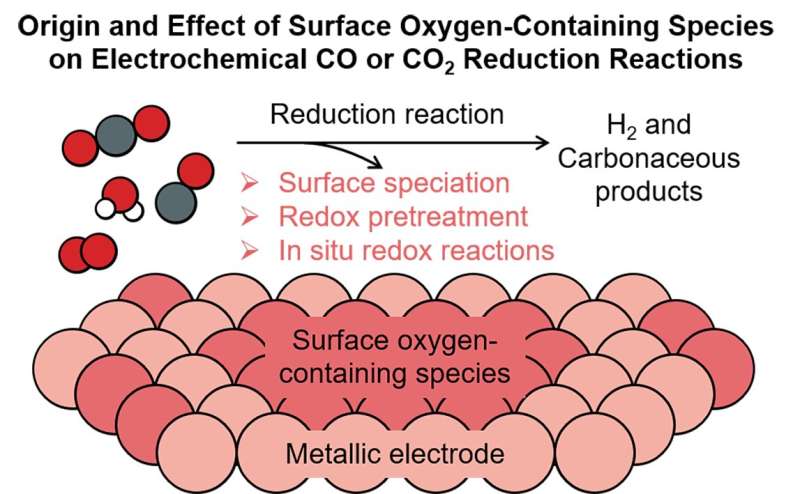
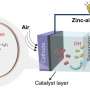
Renewable-energy-powered electrochemical CO or CO2 reduction reactions (CO(2)RR) is one of the most promising strategies to upgrade CO2 to valuable products. A key question and bone of contention is whether any surface or subsurface oxygen remains on the electrocatalysts under the reducing CO(2)RR conditions, and if so, whether that oxygen play any role in facilitating the reaction.
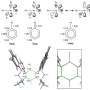
Thermodynamically, the oxides are expected to be reduced to the metallic form under the CO(2)RR conditions according to the Pourbaix diagram. However, multiple experimental studies report evidence for oxygen-containing species on electrocatalysts at CO(2)RR conditions, which could be attributed either to the difference in reaction and characterization conditions, or to the distinct thermodynamic stabilities of surface and bulk oxides.
This mini-review led by Prof. Bingjun Xu (College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University) summarizes recent literature on this topic and discusses the possible sources of oxygen-containing species at or near the electrode-electrolyte interfaces under CO(2)RR conditions.
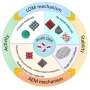
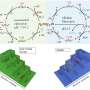
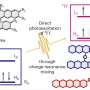
Potential (sub)surface oxygen-containing species are grouped into three main categories based on the conditions at which they are introduced: (1) via the exposure to ambient air; (2) via the pretreatment of the catalyst; and (3) with the assistance of additional oxygen sources via in-situ redox reactions.
Potential impact of oxygen-containing species on the activity and product distribution in the CO(2)RR, and the perspectives on future efforts to reveal the identity and role of oxygen-containing species in the CO(2)RR are also discussed.
The findings are published in the journal Science China Chemistry.
More information: Xiaoxia Chang et al, Origin and effect of surface oxygen-containing species on electrochemical CO or CO2 reduction reactions, Science China Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11426-022-1459-3
Provided by Science China Press