This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
First visible-light induced simultaneous cleavage of C-C and C-N bonds with polyoxometalate photocatalyst
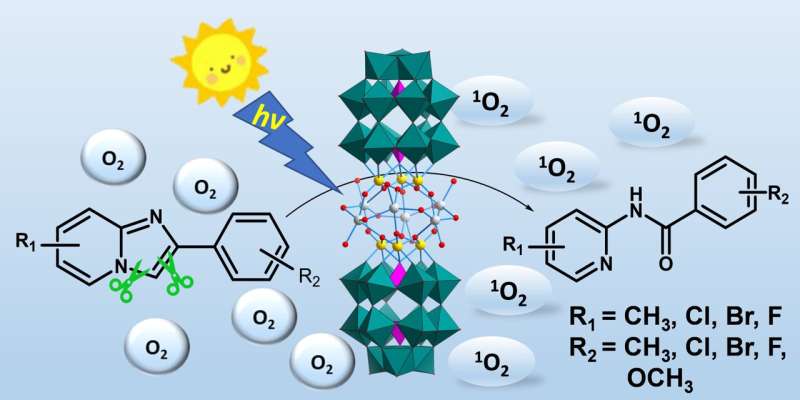
Cracking carbon bonds is a notoriously difficult problem, but it may hold the key to generating greener, more sustainable chemicals. A Chinese research team achieved the first visible-light-promoted simultaneous cleavage of carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds via a silver-modified polyoxometalate photocatalyst, unlocking avenues for applications like carbon-neutral alternatives for fossil fuels. The researchers' findings were published on March 3 in Polyoxometalates.
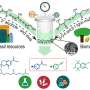
Inexpensive and highly efficient, photocatalytic technology is being used to solve increasingly serious environmental pollution problems. Polyoxometalates (POMs) are a class of metal-oxide clusters with unique physicochemical properties that make them particularly effective in the field of photocatalysis—using light energy to drive a chemical reaction.
Thanks to the stability of their molecular structures and reversible redox properties, POMs as photocatalysts can break down organic pollutants in wastewater and reduce carbon dioxide. POMs can also catalyze simple organic transformations, including bond formation reactions of carbon-carbon (C-C) and carbon-nitrogen (C-N).
However, most of the POMs can only work using ultraviolet light.
"It is of great significance to design and synthesize new visible-light-promoted POMs photocatalysts and explore their potential in new organic reactions," said Shujun Li, study author from Henan Normal University.
With this goal, Li and colleagues explored synthesizing visible-light promoted POMs photocatalysts to wield in selective, simultaneous carbon bond cleaving.
"C-C and C-N bonds are the most widespread and fundamental bonds existing in organic compounds," said Li. "Selectively catalytic cleavage of C–C bonds or C–N bonds for chemical transformations is an important topic in synthetic chemistry and has become one of the most attractive but challenging tasks."
Chemists have pursued this objective over the past few decades because cracking these stubborn bonds might be key to finding valuable new chemicals or more sustainable ways to create known ones. As such, they have developed a variety of catalytic systems to cleave C–C bonds or C–N bonds separately. However, cleavage of both C–C and C–N bonds in a single organic transformation is a challenging objective.
"Few examples of simultaneous cleavage of C-C and C-N bonds in one substrate molecule have been reported so far," said Li.
To make things more complicated, rapid, simultaneous cleavage of these types of bonds requires harsh reaction conditions such as high temperatures and strong oxidizing or initiating agents.
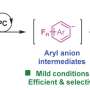
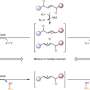
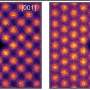
The research team combined niobium (Nb)/tungsten (W) mixed-addendum POM and silver (Ag) ion to obtain a silver-modified polyniobotungstate (Ag-Nb/W).
Ag-Nb/W showed strong absorption in the visible region, which encouraged the researchers to study its catalytic activity under visible light. The researchers' investigations included analysis of substrate scope and bounds of conditions for best performance, as well as the stability and reusability of Ag-Nb/W.
The results indicated that the synthesis and structure of Ag-Nb/W supports efficient catalysis to simultaneously cleave C–C and C–N bonds under visible light in mild conditions. In addition, Ag-Nb/W could be reused up to six times without a reduction in the catalytic activity.
"To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of visible-light-promoted simultaneous cleavage of C-C bond and C-N bond catalyzed by a POM photocatalyst, which coincides with the social demand for green chemistry and sustainable development," said Li.
This work provides a feasible revelation for designing new visible-light-induced polyoxometalates photocatalysts to be used in organic reactions involving the cleavage of C–C and C–N bonds, said Li.
In future steps, the researchers plan to combine this compound with other solid carriers to design a dispersed and more stable photocatalytic material suitable for its applications in photocatalysis.
More information: Shujun Li et al, Silver-modified polyniobotungstate for the visible light-induced simultaneous cleavage of C–C and C–N bonds, Polyoxometalates (2023). DOI: 10.26599/POM.2023.9140024
Provided by Tsinghua University Press