This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Reimagining drugs for a rare brain disorder
A team of researchers has developed a new method to screen FDA-approved drugs to determine if they could be repurposed or improved to help patients with a rare, debilitating disease of the nervous system.
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 5 causes cerebellar neurodegeneration. Loss of coordination, impaired gait and slurred speech are just a few of the debilitating symptoms, which usually emerge between the ages of 20 and 30. There is no cure or even a targeted therapy. SCA5 affects around 1,000 people in the U.S. but is a part of a group of diseases that plagues tens of thousands more.
Despite the nature and broad reach of SCA5 and related diseases, few researchers are trying to find a cure. However, one ataxia-focused research group published a study on Jan. 30 detailing a new method to screen for drugs that might help.
"Not only is there no known therapeutic to treat these diseases, but, to our knowledge, there is no other research campaign to identify potential therapies for a lot of these ataxias," said Robyn Rebbeck, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Minnesota and one of the lead authors on the study.
SCA5 is inherited and is sometimes called "Lincoln's ataxia" because it has been passed down over 10 generations in one family with traces to President Abraham Lincoln's grandparents. It is caused by a mutation in the β-III-spectrin gene, which is critical for creating connections between neurons in the central nervous system.
Adam Avery, the assistant professor at Oakland University who oversaw the work, said, "Our goal is to improve the conditions of these patients within the next 10 to 20 years. … (W)e are family people. We want to provide SCA5 patients and their families with the hope of an effective treatment."
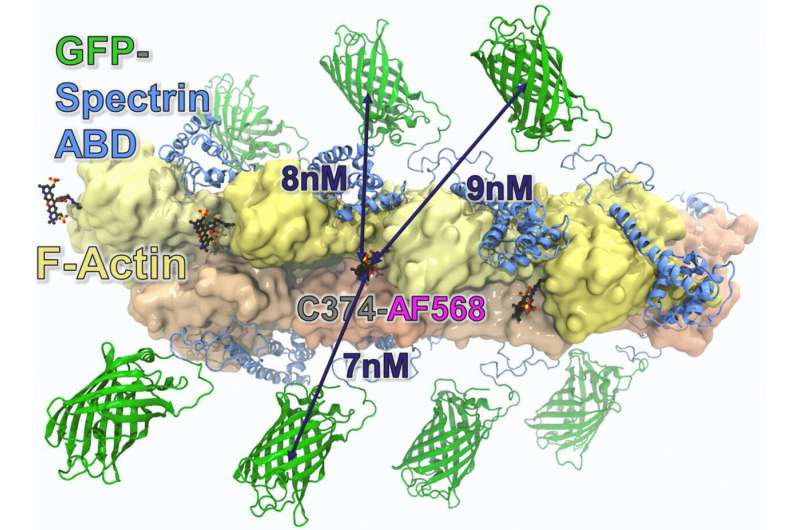
The mutation studied by the researchers causes β-III-spectrin and a structural protein called actin to stick together. This abnormally tight interaction results in a traffic jam inside neurons, which prevents them from carrying out their normal functions, such as controlling speech and movement.
The research team created a pipeline to screen FDA-approved drugs against the mutated β-III-spectrin protein to find out if any can restore its normal function. This assay uses cutting-edge spectroscopy to examine whether and how drugs change the interaction of mutant β-III-spectrin with actin and is at least five-times more sensitive than methods used previously. The drugs that dampen β-III-spectrin's binding to actin initiate a unique florescent signal. This high-throughput screening method allows the team to evaluate 1,536 drugs in about six minutes.
Of the 3,000 FDA-approved drugs analyzed, two immediately stood out to the researchers for their high efficacy and potency: ginsenoside Rb1 and micafungin. However, this is just the beginning. The researchers plan to screen thousands more compounds to get their best shot at finding an effective drug.
Piyali Guhathakurta, an assistant professor at the University of Minnesota and a lead author, said the team is now "primed for screening much larger libraries for compounds that can lead us to drugs that have the potential to treat SCA5. Our assay is the start of the drug-discovery campaign, with collaborators preparing to test these compounds in systems more akin to the human patients that we hope to treat."
The researchers plan to develop a cell culture and mouse model to more definitively test their hits from the drug screen. If the hits are successful in ameliorating disease in future models, they would be that much closer to a drug specific for SCA5 patients.
"Our study is proof that the binding of this mutant spectrin to actin is a druggable target," Avery said. "This work establishes that we can modulate this interaction using small molecule drugs."
Though there is much work to be done, the team is optimistic about the prospects that this new pipeline presents for studying mutations in β-III-spectrin-related proteins that cause other rare diseases like muscular dystrophy.
"Our findings may pave the way for the development of a new class of drugs that will provide relief to patients suffering from SCA5 and additional diseases due to mutations in spectrin-related proteins," Avery explained. "Our technology is adaptable for drug discovery for treatment of other diseases associated with disrupted actin binding."
The paper is published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
More information: Piyali Guhathakurta et al, Early phase drug discovery of β-III-spectrin actin-binding modulators for treatment of spinocerebellar ataxia type 5, Journal of Biological Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102956
Journal information: Journal of Biological Chemistry