This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Examining SIRT6 regulation as a key component of aging
Anti-aging creams, shakes, exercises, you name it, you can read about it online. However, what does science have to say about aging? Ben-Gurion University of the Negev life sciences researcher Dr. Debra Toiber has uncovered what seems to be a key preventive measure of DNA breakdown, which many believe causes aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Dr. Toiber has been focused on a protein called SIRT6, and she has discovered that it seems to have remarkable properties. Its absence seems to downgrade DNA repair significantly.
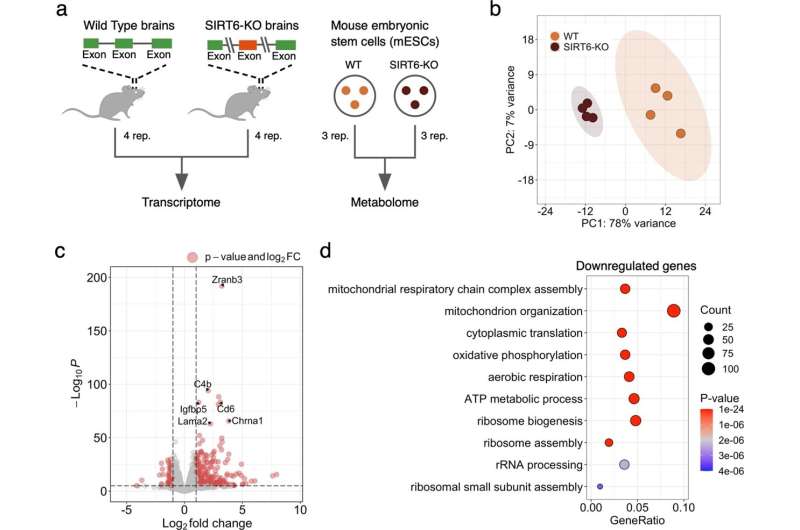
In a new paper just published in Cell Death and Disease, Dr. Toiber and her international colleagues have found that SIRT6 is a key regulator of mitochondrial function in the brain.
"Mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the hallmarks of aging and one of the main characteristics of multiple neurodegenerative diseases. Many defects are observed in the mitochondria's efficiency during aging; however, what initiates these events is unclear," explains Dr. Toiber.
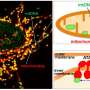
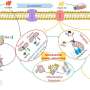
"We found that SIRT6 keeps mitochondria functioning through the transcription regulation of mitochondrial genes," she says.
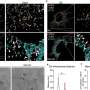
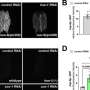
Using transcriptomics, metabolomics, and molecular assays, she and her team observed that in the absence of SIRT6 in the brain, nuclear expressed mitochondrial genes are down-regulated, the number of mitochondria per cell decays, there is an increase in Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) production, and the mitochondrial membrane potential is impaired, causing major metabolic changes.
This effect is partially the result of SIRT6 regulating the expression of the mitochondrial Sirtuins 3 and 4. Importantly, re-introducing SIRT3 and 4 can rescue the membrane potential capacity. Particularly in the brain, during neurodegeneration, mitochondria lose the ability to generate enough Adenosine Tri phosphate (ATP), generate toxic ROS, and impair the production of important metabolites for brain functioning.
"Our results show parallel changes in mitochondrial gene expression induced by the lack of SIRT6 in the brain to the changes observed in aging, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and ALS, suggesting that SIRT6 decay in the brain is the driver of these changes," Dr. Toiber says.
More information: Dmitrii Smirnov et al, SIRT6 is a key regulator of mitochondrial function in the brain, Cell Death & Disease (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05542-w
Journal information: Cell Death and Disease
Provided by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev