This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Agave gene delays poplar dormancy, study finds
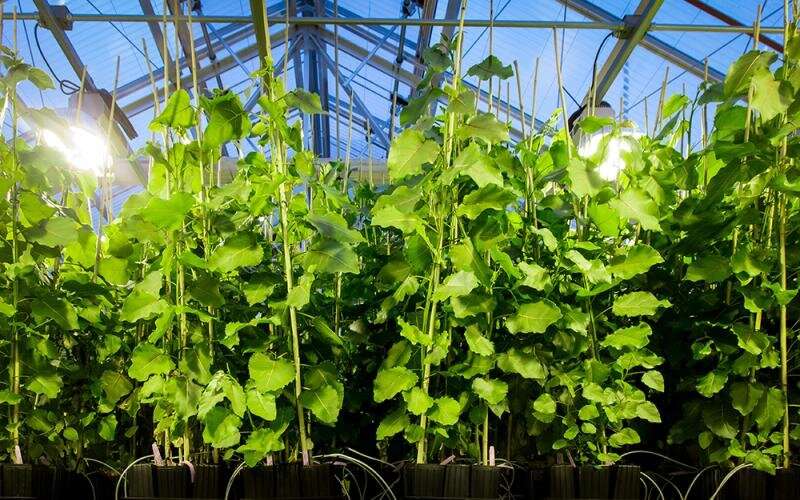

A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory discovered the gene in agave that governs when the plant goes dormant and used it to create poplar trees that nearly doubled in size, increasing biomass yield for biofuels production and carbon sequestration.
By sequencing the messenger RNA of Agave americana, researchers found the REVEILLE1 gene that controls both dormancy and budding. A study showed that poplar engineered with the gene could potentially extend their growing season by two to three months in temperate regions.
Poplar with REVEILLE1 achieved a 166% increase in biomass when grown in a greenhouse, yielding taller trees with larger leaves and thicker stems compared with standard poplars.
"Much like the circadian clock responds to light and dark, REVEILLE genes regulate when plants are asleep in dormancy and when they're awake," said ORNL's Xiaohan Yang. "We used the gene to successfully repress dormancy over two winters."
The findings are published in the journal Plant Physiology.
More information: Degao Liu et al, Agave REVEILLE1 regulates the onset and release of seasonal dormancy in Populus, Plant Physiology (2022). DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiac588
Provided by Oak Ridge National Laboratory