Characterization of poplar budbreak gene enhances understanding of spring regrowth
Trees in temperate climates undergo annual cycles of growth and dormancy corresponding to summer and winter seasons, a critical strategy that allows perennial plants to survive cold and dehydration during the winter months. These important transitions are controlled by the length of the day, or photoperiod, and temperature, but the exact mechanisms by which these annual cycles are initiated in the trees are still poorly understood.
The gene identified and characterized in this study will enhance the understanding of how woody perennial plants begin their growth cycle, enabling development of new approaches to population management, genetic engineering of dormancy-related traits, and breeding trees better adapted to changing environments such as a warmer climate.
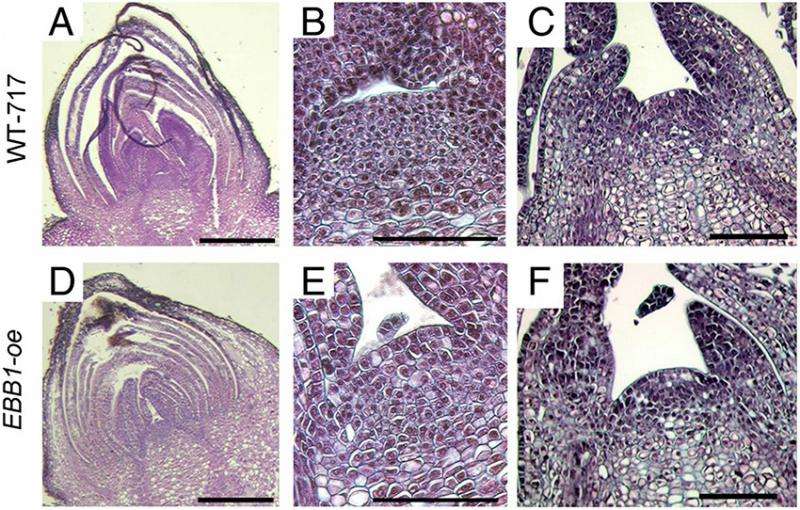
A research team at Michigan Technological University and Oregon State University has identified and functionally characterized a gene called Early Bud-Break 1 (EBB1) in poplar, a bioenergy feedstock. This gene serves as a "master regulator" in the timing of spring growth reactivation, or budbreak. In addition, the protein encoded by EBB1 was found to function in many other processes critical to survival in poplar, including nutrient cycling and root growth.
Results showed that overexpression of the EBB1 gene is sufficient to accelerate bud-burst, whereas down-regulation delays budbreak, enhancing the understanding of dormancy release in woody perennial plants and enabling development of new approaches to breeding trees.
More information: Yordan S. Yordanov et al. EARLY BUD-BREAK 1 () is a regulator of release from seasonal dormancy in poplar trees, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2014). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1405621111
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by US Department of Energy