Efficient electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to nitrogen: Promising way to remove nitrogen from water
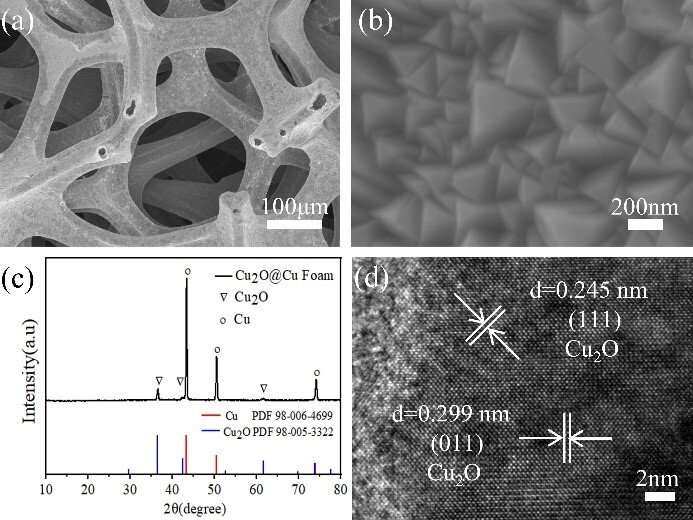
According to a paper recently published in Chemical Communications, Prof. Meng Guowen's group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed an efficient electrocatalytic material to reduce nitrate in water to nitrogen gas, providing a promising way to degrade nitrogen concentration in water.
"This material is a success in improving the selectivity of electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate for N2 in water," said associate Prof. Tang Haibin, who led the study.
Nitrate, a dangerous water pollutant, leads to water eutrophication, water bloom and other ecological and environmental problems. Among nitrate removal methods and technologies, the electrocatalytic reduction method stands out, as it can selectively convert nitrate (NO3-) into ammonium (NH4+) or nitrogen gas (N2), which can effectively reduce the concentration of total nitrogen in water. This phenomenon has applications for restoration of eutrophicated water bodies. However, the materials reported previously, although with preferential selectivity and efficiency toward ammonia/ammonium, are not suitable for application in practical water environments such as lakes and rivers.
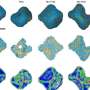
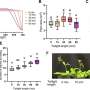
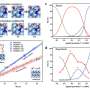
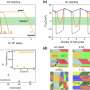
In this study, a (111) preferentially oriented copper oxide (Cu2O) film was prepared on the surface of a porous copper foam framework (Cu2O@CF) by electrochemical deposition. Due to the conductive porous copper foam frame, the composite structure can be easily used as a cathode for electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate. The results showed that the catalytic reduction of nitrate to N2 was significantly improved.
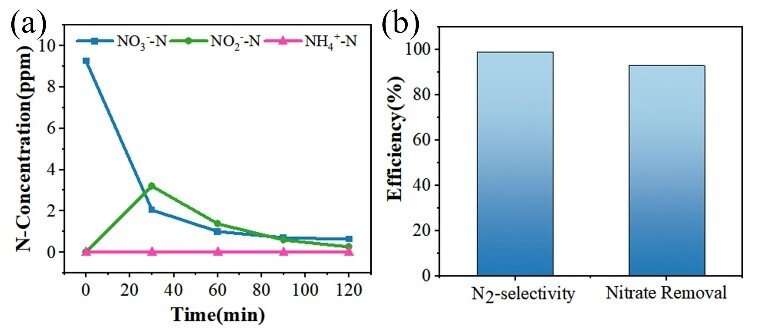
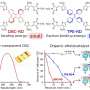
"In alkaline solution, the removal rate of nitrate is 93% and the selectivity of N2 is 99%; and in neutral solution, the removal rate of nitrate was 94.3% and the selectivity of N2 is 49.2%", said Prof. Tang.
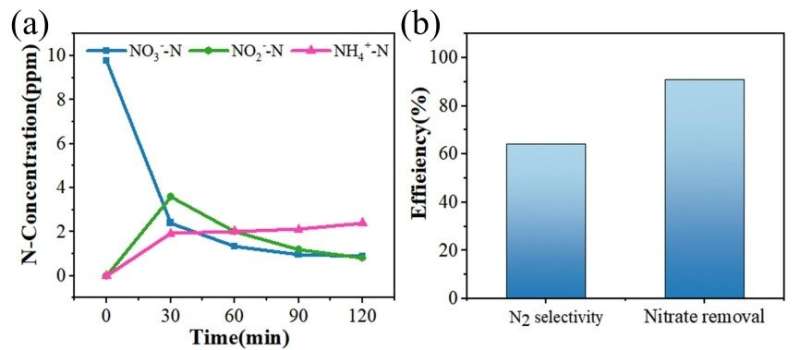
In order to verify the possible interference of other cations and anions in actual water, electrocatalytic tests were carried out using lake water of a local reservoir.
"The removal rate reached as high as 91.1% for nitrate and the selectivity for N2 rose up to 64.2%," said Tang, "both were higher than what we had expected."
The preparation of the cathode material in this study is simple, and it can realize high selectivity for nitrogen gas, indicating the application potential of Cu2O in electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas.
This work provides valuable reference for further designs of stable and efficient electrocatalytic materials to remove nitrogen from water, which is helpful for the treatment and protection of water ecological environment.
More information: Qiangsheng Zhao et al, Efficient electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas by a cubic Cu2O film with predominant (111) orientation, Chemical Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1039/D1CC07299D
Journal information: Chemical Communications
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences