Innovative catalysts examined in expert review

Green hydrogen is an important component in a climate-neutral energy system. It is produced by electrolytically splitting water with wind or solar power and stores this energy in chemical form. But currently, the production of green hydrogen is not yet economical or efficient enough. The key to solving this problem is through the development of innovative electrocatalysts, which should not only work with high efficiencies but should also be available and inexpensive.
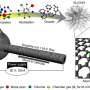
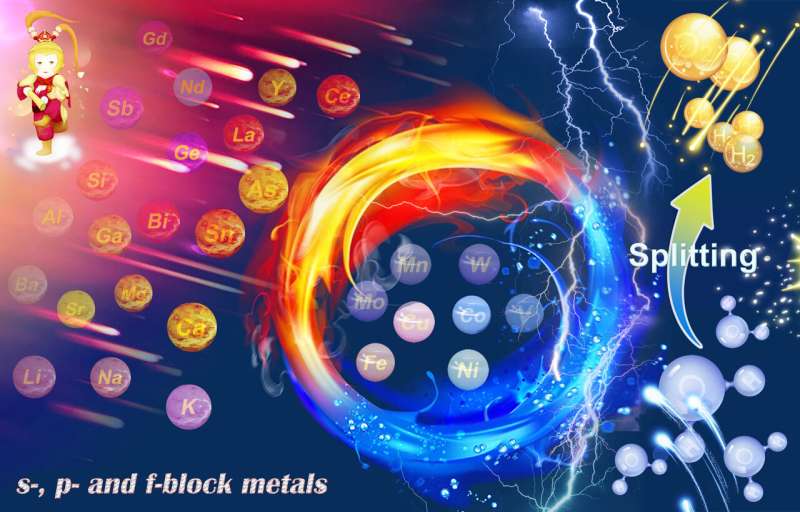
In addition to transition metals, which are already well studied for their catalytic properties, a wider choice of elements has now moved into the focus such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, rare earth metals, lean metals and metalloids. Some of these when combined with transition metal electrocatalysts can significantly improve performance and contribute to the development of next-generation high-performance electrocatalysts.
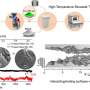
However, many of the processes that take place during electrocatalysis -when oxygen or hydrogen is formed—are still not understood in detail. In a review article, an international team of experts guides us through this exciting research field and draws a perspective, sketching the next steps catalyst research could take. "This contribution summarizes the current state of knowledge on such unconventional s-, p-, and f-block metal-based materials and makes it comprehensible to a wider community of scientists", Dr. Prashanth W. Menezes points out and adds: "Further, the essential role of such metals during water splitting electrocatalysis is described in great depth, as well as the modification strategy that should be considered when one wants to utilize them to mediate non-noble-based electrocatalysts. We hope to significantly accelerate research and development of novel, innovative catalyst materials with this review article."
The research was published in Advanced Materials.
More information: Ziliang Chen et al, The Pivotal Role of s‐, p‐, and f‐Block Metals in Water Electrolysis: Status Quo and Perspectives, Advanced Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202108432
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres