Cell's energy secrets revealed with supercomputers
It takes two to tango, as the saying goes.
This is especially true for scientists studying the details of how cells work. Protein molecules inside a cell interact with other proteins, and in a sense the proteins dance with a partner to respond to signals and regulate each other's activities.
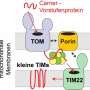
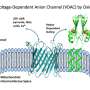
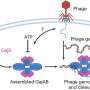
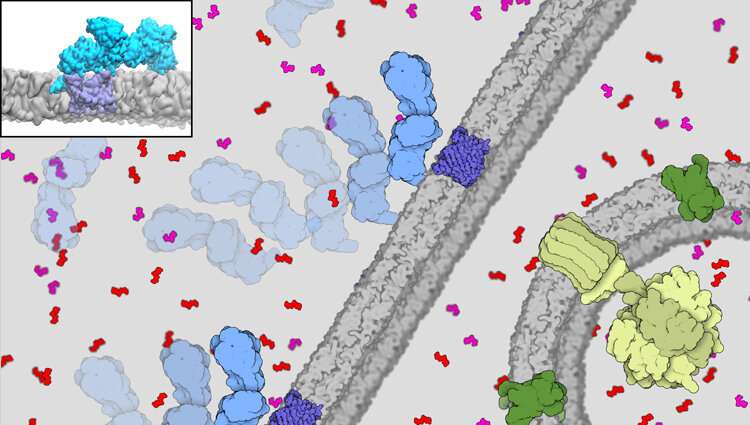
Crucial to giving cells energy for life is the migration of a compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) out of the cell's powerhouse, the mitochondria. And critical for this flow out to the power-hungry parts of the cell is the interaction between a protein enzyme called hexokinase-II (HKII) and proteins in the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) found on the outer membrane of the mitochondria.
Supercomputer simulations have revealed for the first time how VDAC binds to HKII. The work was supported by allocations awarded by the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE) on the Stampede2 system of the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC). XSEDE is funded by the National Science Foundation.
This basic research in how proteins interact out of the cell's powerhouses, the mitochondria, will help researchers understand the molecular basis of diseases such as cancer.
"We had strong evidence that they bind, but we didn't know how they bind to each other," said Emad Tajkhorshid, the J. Woodland Hastings Endowed Chair in Biochemistry at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "That was the million-dollar question."
Tajkhorshid co-authored a study published in Nature Communications Biology in June 2021. The study found that when the enzyme and the channel proteins bind to each other, the conduction of the channel changes and partially blocks the flow of ATP. Simulations on the Stampede2 system of TACC revealed this binding.
What's more, the XSEDE-allocated Ranch system at TACC holds the off-site permanent file storage for the study's data.
"If it wasn't for XSEDE, we wouldn't be studying many of these complex projects and biological systems because you simply can't afford running the simulation. They usually require long simulations, and we need multiple copies of these simulations to be scientifically convincing. Without XSEDE it is impossible. We would have to go back to studying smaller systems," Tajkhorshid said.
This work has implications for a deeper understanding of not only healthy cells, but cancer cells.
Basically, a cell needs ATP to metabolize glucose. It uses the 'P' to convert glucose to glucose phosphate, giving it a 'handle' that the cell can use. Hexokinase-II makes the conversion happen, binding at the mitochondrial channel to gobble up the ATP and phosphorylate it.
"We showed how the phosphorylation affects this process of binding between the two proteins. That was also verified experimentally," Tajkhorshid said.
The VDAC channel is critical for efficient delivery of ATP directly to hexokinase. "It can work like a double-edged sword. For a healthy cell it's good. For a cancer cell, it also helps the cell to promote and to proliferate," he said.
Tajkhorshid's team developed the most detailed and sophisticated model yet of the complex formed by the binding of HKII and VDAC, combining highest-resolution all-atom molecular dynamics simulations with coarser Brownian dynamics techniques. The system size of the VDAC-HKII complex was about 700,000 atoms, including the membrane. It's about one-fifth of the diameter of the COVID-19 virus.
"What stands out in our approach is that we actually considered the cellular background of this interaction," said Po-Chao Wen, a post-doctoral research associate at the NIH Center for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.

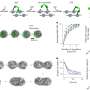
Wen explained that their simulation design started with the hypothesis that the VDAC protein in the outer membrane might interact at all with HKII, which is localized at a different part of the cell called the cytosol. They speculated that HKII should bind first to the membrane, drifting on it until it reaches a VDAC protein.
VDAC sitting on the membrane has already been well modeled, and the researchers built on this knowledge to break down the modeling of the HKII-VDAC complex into three parts, which initially focused on HKII.
To study how HKII binds to the mitochondrial outer membrane, they used all-atom molecular dynamics and a tool developed by their center called the Highly Mobile Membrane Model (HMMM), which deals with the membrane interaction.
They next used Brownian dynamics to study how HKII drifts on the membrane to meet VDAC, creating many encounter/collision events between a sitting VDAC and a drifting HKII on a planar membrane.
"Then we used all-atom molecular dynamics to get a more refined model and specific size of the interaction to look for this particular protein-protein interaction," Wen added. This helped them find the most stable complex of the two proteins formed.
"It seemed almost impossible when we started this process, because of the long timescales of milliseconds to seconds of the all-atom simulations," said study co-author Nandan Haloi, a PhD student also at the center.
Many other computational science tools were developed by the group, including the commonly-used NAMD for molecular dynamics.
"These are really expensive calculations, which would require millions of dollars to set up independently. And you need to run on parallel supercomputers using our NAMD code, otherwise we could not reach the time scales that we needed," Tajkhorshid said.
"We're extremely happy with TACC and their support for not only just this work, but most of our projects and also our software development, tuning the software and making it faster. TACC has been wonderful in supporting us," Tajkhorshid said.
TACC scientists work with the NIH Center for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics to constantly optimize the NAMD software, currently used by thousands of researchers.
The next steps in the research include more ambitious systems such as the fusion of two cells, important in understanding how neurons in the brain fire signals to each other; and how a virus such as the novel coronavirus fuses to the host cell.
Tajkhorshid's group was awarded a Leadership Resource Allocation on the NSF-funded flagship supercomputer Frontera at TACC to investigate some of these ambitious projects.
Tajkhorshid said that they "like to look at our work as a computational microscope that allows one to look at molecular systems and processes, how molecules come together, how they move, and how they change their structure to accomplish a particular function that people have been indirectly measuring experimentally. Supercomputers are essential in providing this level of detail, which we can use to understanding the molecular basis of diseases, drug discovery, and more."
More information: Nandan Haloi et al, Structural basis of complex formation between mitochondrial anion channel VDAC1 and Hexokinase-II, Communications Biology (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02205-y
Journal information: Communications Biology
Provided by Texas Advanced Computing Center