Early humans were sheltered from worst effects of volcanic supereruption

A massive volcanic eruption in Indonesia about 74,000 years ago likely caused severe climate disruption in many areas of the globe, but early human populations were sheltered from the worst effects, suggests a new study published in the journal PNAS.
The eruption of the Toba volcano was the largest volcanic eruption in the past 2 million years, but its impacts on climate and human evolution have been unclear. Resolving this debate is important for understanding environmental changes during a key interval in human evolution.
"We were able to use a large number of climate model simulations to resolve what seemed like a paradox," said lead author Benjamin Black from Rutgers University. "We know this eruption happened and that past climate modeling has suggested the climate consequences could have been severe, but archaeological and palaeoclimate records from Africa don't show such a dramatic response.
"Our results suggest that we might not have been looking in the right place to see the climate response. Africa and India are relatively sheltered, whereas North America, Europe and Asia bear the brunt of the cooling. One intriguing aspect of this is that Neanderthals and Denisovans were living in Europe and Asia at this time, so our paper suggests evaluating the effects of the Toba eruption on those populations could merit future investigation."
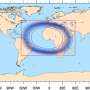
The researchers analysed 42 global climate model simulations in which they varied magnitude of sulphur emissions, time of year of the eruption, background climate state and sulfur injection altitude to make a probabilistic assessment of the range of climate disruptions the Toba eruption may have caused.
The results suggest there was likely significant regional variation in climate impacts. The simulations predict cooling in the Northern Hemisphere of at least 4 degrees Celsius, with regional cooling as high as 10 degrees Celsius depending on the model parameters.
In contrast, even under the most severe eruption conditions, cooling in the Southern Hemisphere—including regions populated by early humans—was unlikely to exceed 4 degrees Celsius, although regions in southern Africa and India may have seen decreases in precipitation at the highest sulphur emission level.
The results explain independent archaeological evidence suggesting the Toba eruption had modest effects on the development of hominid species in Africa. According to the authors, their ensemble simulation approach could be used to better understand other past and future explosive eruptions.
"Our work is not only a forensic analysis of Toba's aftermath some 74,000 years ago, but also a means of understanding the unevenness of the effects such very large eruptions may have on today's society," said co-author Dr. Anja Schmidt from the University of Cambridge. "Ultimately, this will help to mitigate the environmental and societal hazards from future volcanic eruptions."
More information: Global climate disruption and regional climate shelters after the Toba supereruption. PNAS (2021). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2013046118
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by University of Cambridge