Strong M-M' Pauli repulsion leads to repulsive metallophilicity
A research team led by Professor Chi-Ming Che and Dr. Jun Yang, from the Research Division for Chemistry and Department of Chemistry at the Faculty of Science of the University of Hong Kong, has resolved a long-standing fundamental problem in the field of metal-metal closed-shell interaction. This work has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
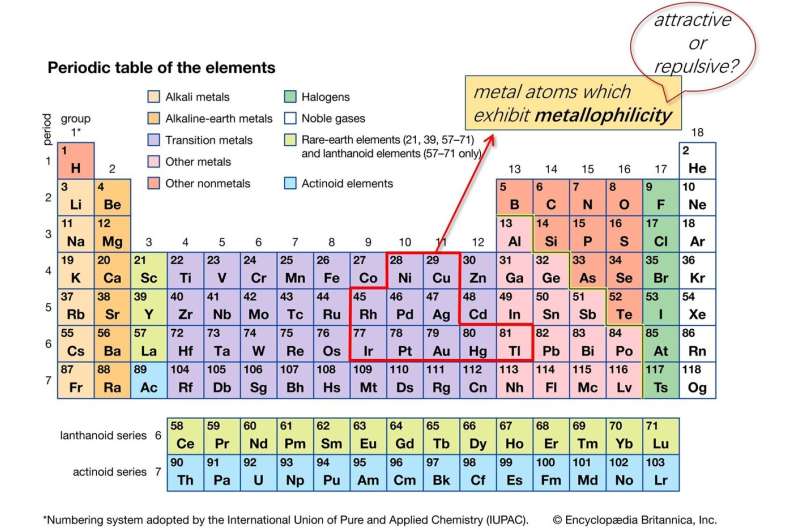
Metal-Metal closed-shell interaction, also known as metallophilicity, has a huge impact in diverse fields of chemistry, such as supramolecular chemistry and organometallic chemistry. Early reports on metallophilicity could be traced back to the 1970s. Many leading theoretical chemists around the world made contributions in the field, such as Roald Hoffmann (1981 Nobel Laureate in Chemistry), Pekka Pyykkӧ, etc.. Metallophilicity is important in the fabrication of self-assemblies by transition metal complexes, which has demonstrated profound applications in organic semiconductors, bio-sensing and functional optoelectronic materials.
Going beyond conventional wisdom
The term "metallophilicity" originated from Europe and has been extensively used by chemists as a guiding principle in molecular design studies and to rationalize the spectroscopic properties of transition metal complexes. Up to now, the general consensus of metallophilicity in the academic community is "attractive," which has been conceived to come from orbital hybridization and/or relativistic effect of heavy metal atom, such as gold or platinum (3rd row metal in the elemental table). Together with Professor Che and Dr. Yang, Postdoctoral Fellow Dr. Qingyun Wan and co-workers questioned the conventional wisdom of coordination chemists, concluding that the metallophilicity is not an attractive interaction in organometallic complex, but is actually repulsive in nature due to strong M-M' Pauli repulsion.
They performed a combined theoretical and experimental research on metallophilicity and observed strong M-M' Pauli repulsion in organometallic complex having closed-shell electronic configurations, which will provide a new theoretical perspective on the possibility of making new supramolecular materials with inexpensive earth-abundant transition metal complexes, such as that of palladium or silver or nickel (1st or 2nd row metals in the elemental table). It is also a crucial achievement in the fundamental understanding of weak intermolecular interactions.
Background and achievement
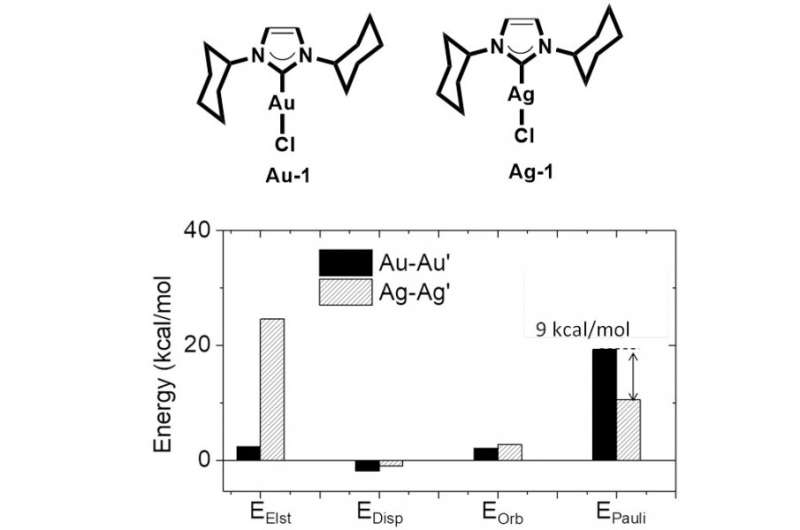
In the microworld of small molecules, there are many types of interactions. Metallophilicity describes the interaction between metal atoms as having closed-shell electronic configurations. In the early 1970s, chemists observed an interesting phenomenon that two closed-shell metal atoms could form a short metal-metal distance. A special "attraction" was proposed to exist between two metal atoms, pushing two metal atoms coming close. Many theoretical models were raised to account for such an attachment, such as the model of orbital hybridization or relativistic effect of the heavy metal. However, these theoretical models have conflictions with some experiment observations, like the relatively shorter Ag-Ag distance in Ag complexes compared to the Au-Au distance in the Au analogs. Thus, this problem has remained controversial for a long time and always plagued inorganic and theoretical chemists.
The researchers at HKU used high-level calculation methods and experimental techniques to investigate such a tough problem, and proved that the metallophilicity is repulsive in nature due to strong M-M' Pauli repulsion. They concluded that orbital hybridization and relativistic effect would strengthen the metal-metal Pauli repulsion when forming a close metal-metal contact. Intermolecular dispersion and electrostatic interaction will counter-balance the metal-metal repulsion, leading to a short metal-metal distance. This theoretical model could well explain why Ag-Ag distance is shorter than the Au-Au distance, due to weaker Ag-Ag Pauli repulsion which is induced by less orbital hybridization in the Ag complex.
By a conservative estimation, there were more than 5,000 papers published in the literature related to "attractive metallophilicity." The statement of "repulsive metallophilicity" is first proposed by the research team in their recent PNAS publication. This work was also recognized by Professor Harry Gray in Caltech, who was awarded the Wolf Prize in Chemistry in 2004, one of the most honorable awards in the field.
More information: Qingyun Wan et al, Strong metal–metal Pauli repulsion leads to repulsive metallophilicity in closed-shell d8 and d10 organometallic complexes, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2020). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2019265118
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by The University of Hong Kong