Tomato plants communicate at a molecular level

Working together with researchers from the University of Tübingen, the University of Tromsø, UC Davis and the Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich, biologists from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have discovered how tomato plants identify Cuscuta as a parasite. The plant has a protein in its cell walls that is identified as "foreign" by a receptor in the tomato.
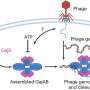
Cuscuta spp., also known as dodder, is a parasitic vine which grafts to the host plant using special suckers to obtain water, minerals and carbohydrates. The parasite also attacks and damages crops such as oilseed rape, sweetcorn, soy, flax or clover. Although the infection generally goes undetected by the host, some species of tomato actively defend themselves by forming wooden tissue which prevents the suckers from penetrating the plant. In earlier research, the biologists at FAU discovered that these tomatoes possess a special receptor, the Cuscuta receptor 1 (CuRe1), which triggers the defense mechanism. However, until now, it was unclear how the receptor recognizes the danger posed by the dodder.
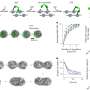
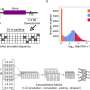
The researchers have now succeeded in answering this question: The dodder possesses a specific marker in its cellular wall, a glycine-rich protein (GRP). Using its receptor CuRe1, the tomato is able to recognize the molecular pattern of the GRP and identify the dodder as a pathogen, and triggers the immune reaction as a result. The new findings concerning the molecular dialog between the Cuscuta marker and the tomato receptor may help to increase the resistance of crop plants against parasitic plants.
More information: Volker Hegenauer et al, The tomato receptor CuRe1 senses a cell wall protein to identify Cuscuta as a pathogen, Nature Communications (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19147-4
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Erlangen-Nuremberg