Researchers make green chemistry advance with new catalyst for reduction of carbon dioxide
Researchers at Oregon State University have made a key advance in the green chemistry pursuit of converting the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide into reusable forms of carbon via electrochemical reduction.
Published in Nature Energy, the study led by Zhenxing Feng of the OSU College of Engineering and colleagues at Southern University of Science and Technology in China and Stanford University describes a new type of electrocatalyst.
The catalyst can selectively promote a CO2 reduction reaction resulting in a desired product—carbon monoxide was the choice in this research. A catalyst is anything that speeds the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
"The reduction of carbon dioxide is beneficial for a clean environment and sustainable development," said Feng, assistant professor of chemical engineering. "In contrast to traditional CO2 reduction that uses chemical methods at high temperatures with a high demand of extra energy, electrochemical CO2 reduction reactions can be performed at room temperature using liquid solution. And the electricity required for electrochemical CO2 reduction can be obtained from renewable energy sources such as solar power, thus enabling completely green processes."
A reduction reaction means one of the atoms involved gains one or more electrons. In the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, metal nanocatalysts have shown the potential to selectively reduce CO2 to a particular carbon product. Controlling the nanostructure is critical for understanding the reaction mechanism and for optimizing the performance of the nanocatalyst in the pursuit of specific products, such as carbon monoxide, formic acid or methane, that are important for other chemical processes and products.
"However, due to many possible reaction pathways for different products, carbon dioxide reduction reactions have historically had low selectivity and efficiency," Feng said. "The electrocatalysts need to promote the reaction with high selectivity to get one certain product, carbon monoxide in our case. Despite many efforts in this field, there had been little progress."
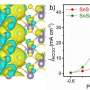
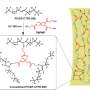
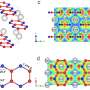
Feng and his research co-leaders tried a new strategy. They made nickel phthalocyanine as a molecularly engineered electrocatalyst and found it showed superior efficiency at high current densities for converting CO2 to carbon monoxide in a gas-diffusion electrode device, with stable operation for 40 hours.
"To understand the reaction mechanism of our catalyst, my group at OSU used X-ray absorption spectroscopy to monitor the catalyst's change during the reaction processes, confirming the role of the catalyst in the reaction," Feng said. "This collaborative work demonstrates a high-performance catalyst for green processes of electrochemical CO2 reduction reactions. It also sheds light on the reaction mechanism of our catalyst, which can guide the future development of energy conversion devices as we work toward a negative-carbon economy."
More information: Xiao Zhang et al, Molecular engineering of dispersed nickel phthalocyanines on carbon nanotubes for selective CO2 reduction, Nature Energy (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-0667-9
Journal information: Nature Energy
Provided by Oregon State University