Improved 3-D nanoprinting technique to build nanoskyscrapers
Nanowalls, nanobridges, nano "jungle gyms": It could seem like the description of a Lilliputian village, but these are actual 3-D-printed components with potential applications in nanoelectronics, smart materials and biomedical devices. Researchers at the Center for Soft and Living Matter (CSLM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea) have improved a 3-D nanoprinting process that produces self-stacked, tall, narrow nanostructures.
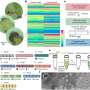
As shown in their latest publication in Nano Letters ("Near-field electrospinning for three-dimensional stacked nanoarchitectures with high aspect ratios"), the team also used this technique to produce transparent nanoelectrodes with high optical transmission and controllable conductivity.
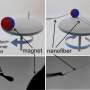
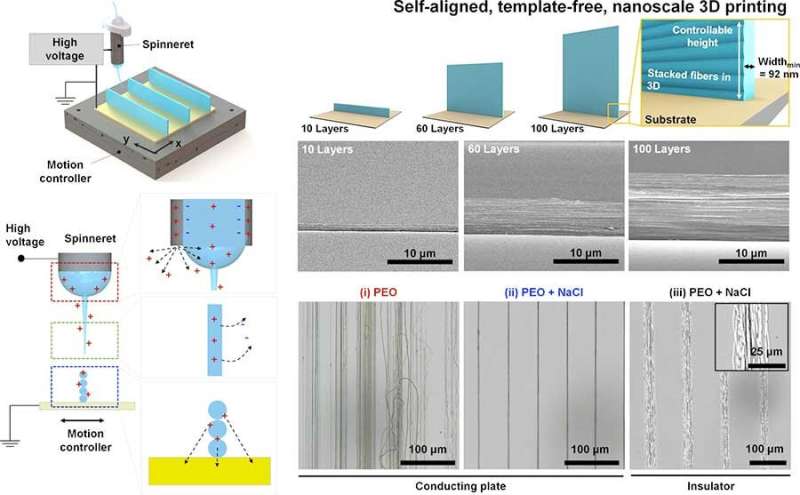
The near-field electrospinning (NFES) technique consists of a syringe filled with a polymer solution suspended above a platform, which collects the ejected nanofiber and is pre-programmed to move left-and-right, back-and-forth, depending on the shape of the desired final product. The syringe and the platform have opposite charges so that the polymer jet emerging from the needle is attracted to the platform, forming a continuous fiber that solidifies on the platform.
Since the electrospun jets are difficult to handle, this technique was limited to two-dimensional (2-D) structures or hollow cylindrical three-dimensional (3-D) structures, often with relatively large fiber diameters of a few micrometers.
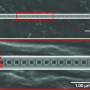
IBS researchers were able to achieve better control of the nanofiber deposition on the platform by adding an appropriate concentration of sodium chloride (NaCl) to the polymer solution. This ensured the spontaneous alignment of the nanofiber layers stacked on top of each other forming walls.
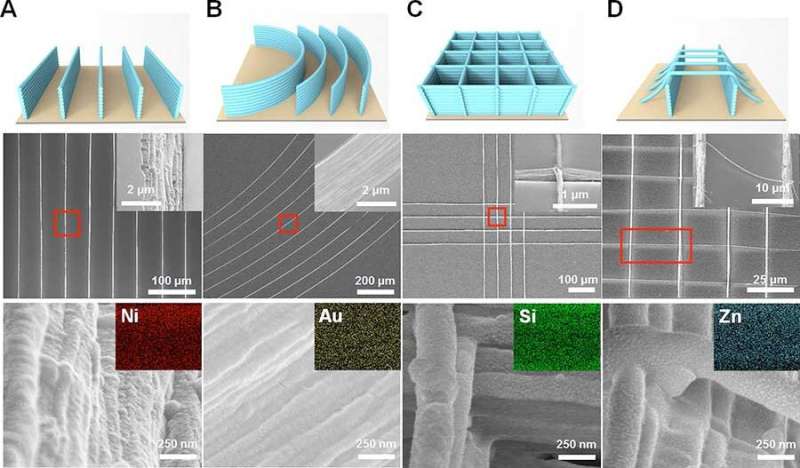
"Although it is highly applicable to various fields, it is difficult to build stacked nanofibers with multiple designs using the conventional electrospinning techniques," says Yoon-Kyoung Cho, the corresponding author of the study. "Our experiment showed that salt did the trick."
The benefit provided by salt is related to the charges. The difference in voltage between the syringe and the platform creates positive charges in the polymer solution and negative charges in the platform, but a residual positive charge stays in the solidified fibers on the platform. The team found that applying salt to the polymer solution enhances the charge dissipation, leading to higher electrostatic attraction between the nanofiber jet and the fibers deposited on the platform.
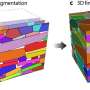
Based on this mechanism, the team was able to produce tall-and-narrow nanowalls with a minimum width of around 92 nanometers and a maximum height of 6.6 micrometers, and construct a variety of 3-D nanoarchitectures, such as curved nanowall arrays, nano "jungle gyms," and nanobridges with controllable dimensions.
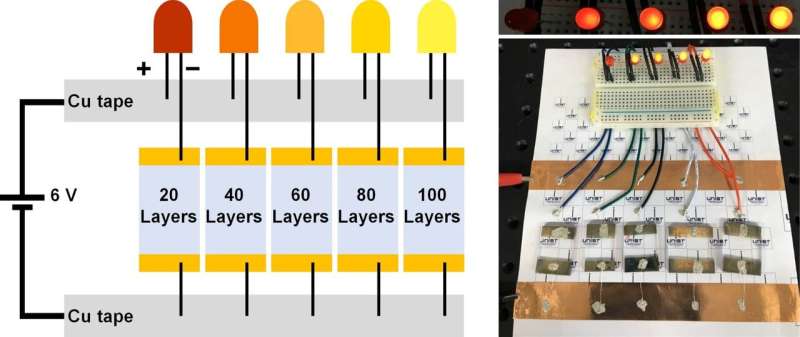
To demonstrate the potential application of these nanostructures, the researchers in collaboration with Hyunhyub Ko, professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), prepared 3-D nanoelectrodes with silver-coated nanowalls embedded in transparent and flexible polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) films. They confirmed that electrical resistance could be tuned with the number of nanofiber layers (the taller the nanowalls, the smaller the resistance), without affecting light transmission.
"Interestingly, this method can potentially avoid the trade-off between optical transmittance and sheet resistance in transparent electrodes. Arrays of 3-D silver nanowires made with 20, 40, 60, 80, or 100 layers of nanofibers had variable conductivity, but stable light transmission of around 98 percent," concludes Yang-Seok Park, the first author of the study.
More information: Yang-Seok Park et al. Near-Field Electrospinning for Three-Dimensional Stacked Nanoarchitectures with High Aspect Ratios, Nano Letters (2019). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04162
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by Institute for Basic Science