Single cell transcriptomics: A new sequencing approach
Researchers from University of Southern Denmark, Wellcome Sanger Institute and BGI have published a study in the journal Genome Biology comparing the library preparation and sequencing platforms for single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq).
Single cell transcriptomics (i.e. scRNA-seq) is a next-generation sequencing approach that simultaneously measures the messenger RNA concentrations of thousands of genes in individual cells. This enables researchers to gain a high-resolution view of cells to unravel heterogeneous cell populations and better understand individual cell functions in the body. Although several single-cell protocols exist, the sequencing has traditionally been performed using Illumina technology and sequencing platforms.
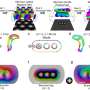
The authors performed the first comparison of traditional Illumina platforms to an alternative BGISEQ-500 short-read sequencing platform for single-cell transcriptomics. The authors profiled 468 individual cells by scRNA-seq using two different protocols (SMARTer and Smart-seq2), generating 1297 single-cell libraries for sequencing across both Illumina HiSeq and BGISEQ-500 platforms. By using two different cell types (Human immortalized leukemia cells "K562' and mouse embryonic stem cells 'mESCs') and spiking synthetic RNA control sequences, the authors benchmarked the performance between sequencing platforms. The study found that BGISEQ-500 was highly comparable in sensitivity, accuracy and reproducibility of detected RNA molecules to the Illumina platform
Although sequencing reagents and personnel costs are subject to geographical constraints, BGISEQ-500 typically has higher data throughput at slightly lower costs. "The combination of higher throughput with marginally increased cost per lane makes the BGISEQ-500 an attractive alternative for scRNA-seq projects, where significant multiplexing is required alongside considerable read depth per cell," notes Dr. Miaomiao Jiang, BGI's co-lead author on the paper.
"This is the first study to compare Illumina HiSeq with BGISeq-500 sequencing platform for single-cell RNA-sequencing, offering researchers with an alternative sequencing option. Our study finds very similar performance in the compared metrics between the platforms. This would be extremely useful for large scale single-cell sequencing initiatives, generating reference maps of all human cell types and enhancing our understanding of human health."
Dr. Kedar Natarajan is the lead and co-corresponding author on the paper. Dr. Natarajan heads his single-cell group at Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at SDU.
More information: Kedar Nath Natarajan et al. Comparative analysis of sequencing technologies for single-cell transcriptomics, Genome Biology (2019). DOI: 10.1186/s13059-019-1676-5
Journal information: Genome Biology
Provided by University of Southern Denmark