February 2, 2018 feature
New quantum repeater paves the way for long-distance big quantum data transmission
Physicists have designed a new method for transmitting big quantum data across long distances that requires far fewer resources than previous methods, bringing the implementation of long-distance big quantum data transmission closer to reality. The results may lead to the development of future quantum networks, such as a global-scale quantum internet.
The researchers, Michael Zwerger and coauthors at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, have published a paper on the new long-range quantum communication method in a recent issue of Physical Review Letters.
"The greatest significance of our work is that we provide an efficient and scalable scheme for long-distance quantum communication," Zwerger told Phys.org. "We believe that this will be an essential ingredient for a future quantum internet, where large amounts of quantum data will be transmitted. Most importantly, in contrast to previous proposals, the required resources (per transmitted qubit) at each repeater station do not scale with the distance, which makes the quantum data transmission more efficient."
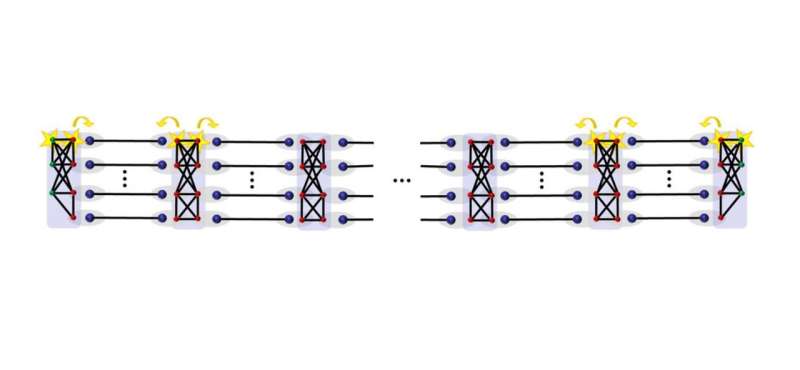
The new method relies on an alternative type of quantum repeater—a device that generates quantum entanglement at distant locations on a quantum network in order to combat signal loss, somewhat how an amplifier boosts the signal in classical communication networks.
The biggest advantage of the new quantum repeater is that it can allow quantum data transmission to be scaled up to longer distances much more easily than with previous quantum repeaters. Typically, as the transmission distance increases, more resources (qubits) are needed at each repeater station. In previous schemes, the number of resources grows polylogarithmically or even polynomially at each repeater station with the distance.
Using the new quantum repeater, the number of resources per transmitted qubit remains constant at each repeater station; that is, it is entirely independent of the distance. This allows for quantum data to be transmitted over arbitrarily long distances using a relatively small amount of resources. In its current implementation, the method uses a few hundred qubits at each repeater station, and can reach intercontinental distances.
As the physicists explain, the key behind the new quantum repeater is an entanglement distillation protocol called hashing, which generates perfect pairs of entangled qubits. The researchers also used an optimized measurement-based implementation, which greatly reduces unwanted noise. These tools provide a high error tolerance and high transmission rates, allowing for quantum data transmission in realistically noisy scenarios, such as a quantum internet.
"Just think of the internet as it has grown over the years, where data transmission has increased dramatically," Zwerger said. "One can envision a quantum internet, where rather than classical data quantum information is transmitted. Indeed, a number of very interesting applications of such quantum data transmission have been discussed, among them quantum cryptography, distributed quantum computing and distributed sensing. Truly secure transmission requires large keys, and hence also large quantum transmission rates. A similar thing can be said about the possibility of distributed quantum computation. In early proof-of-principle experiments, rates and overheads might not be a big deal, but this for sure will become highly relevant once one scales things up. This is where our proposal becomes relevant."
In the future, the researchers plan to extend the new quantum repeater devices to work with larger networks.
"The present proposal is for point-to-point communication between a sender and a receiver," Zwerger said. "We plan to use similar ideas for multipartite quantum networks with many users. In addition, we are currently investigating novel schemes where we try to apply similar techniques on smaller scales—taking some of the ideas of the hashing protocol and design entanglement purification protocols and communication schemes that use only a few qubits. This might have an impact on a shorter timescale, when first prototype quantum communication systems will be built."
More information: M. Zwerger, A. Pirker, V. Dunjko, H.J. Briegel, and W. Dür. "Long-Range Big Quantum-Data Transmission." Physical Review Letters. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.030503 . Also at arXiv:1705.02174 [quant-ph]
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
© 2018 Phys.org