Study reveals new method to develop more efficient drugs

A new study led by University of Kentucky researchers suggests a new approach to develop highly-potent drugs which could overcome current shortcomings of low drug efficacy and multi-drug resistance in the treatment of cancer as well as viral and bacterial infections.
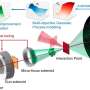
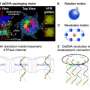
Published in Nanomedicine, the study identified a new mechanism of targeting multi-subunit complexes that are critical to the function of viruses, bacteria or cancer, thus reducing or possibly even eliminating their resistance to targeted drugs.
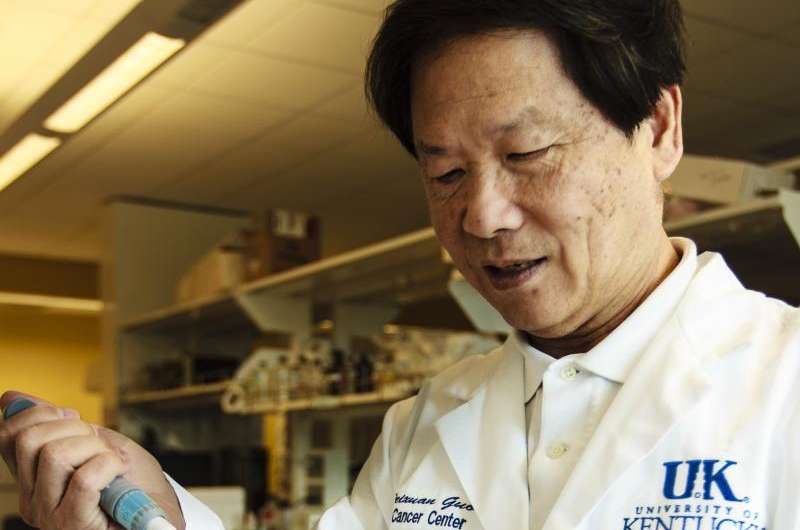
The study was led by Peixuan Guo, director of UK's Nanobiotechnology Center and one of the top nanobiotechnology experts in the world. Guo holds a joint appointment at the UK Markey Cancer Center and in the UK College of Pharmacy.
"Efficacy is the key in drug development," Guo said. "Inhibiting multisubunit targets works similar to the series-circuit Christmas decorating light chains; one broken bulb turns off the entire lighting system."
By targeting RNA or protein subunits that have multiple sites for inactivation, but that are inextricably linked, this method allows for killing or disabling the RNA or protein without requiring the inhibition of multiple pathways that might be used by the organism to remain active and viable (and thus, multiple drugs are not needed, as well). Using this method, a single subunit targeting to the target RNA or protein subunits that is unique and assenting for the organism, the organism will be disabled or die and thus, no longer able to cause disease.
"One of the vexing problems in the development of drugs is drug resistance," said Tim Tracy, former Dean of the UK College of Pharmacy and current UK provost. "Dr. Guo's study has identified a new mechanism of efficiently inhibiting biological processes that are critical to the function of the disease-causing organism, such that resistance is minimized or eliminated."
More information: "New approach to develop ultra-high inhibitory drug using the power function of the stoichiometry of the targeted nanomachine or biocomplex." Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015 Jul;10(12):1881-97. DOI: 10.2217/nnm.15.37
Journal information: Nanomedicine
Provided by University of Kentucky