Trapping free electrons with polycyclic aromatic molecules creates better materials
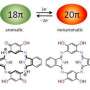
Replacing traditional semiconductors with flexible and lightweight organic components has the potential to realize significant cost savings for manufacturers. Recently, a promising class of organic materials known as open-shell polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) has gained researchers' attention (see image). These molecules consist of interlocked, benzene-like rings and contain unpaired electrons, or 'free-radical' centers. Interactions between the radical centers and aromatic electrons make these compounds extremely responsive to light- and electron-based stimuli. Unfortunately, these same radical electrons can quickly degrade PAH chemical structures, rendering them unusable.
Jishan Wu from the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering in Singapore and an international team of co-workers have now devised a new stabilization strategy that promises to make open-shell PAHs even more practical. Through clever modification of a prototypical compound known as Chichibabin's hydrocarbon, the team has produced two types of PAHs that retain active radical centers for unprecedented amounts of time.
Chichibabin's hydrocarbon has a sextet of aromatic rings that thermodynamically stabilize radical centers. However, it also has a strong chemical affinity for oxygen atoms and tends to polymerize in their presence. To resolve this issue, Wu and co-workers used a process known as benzannulation to add four additional aromatic benzene rings to the PAH framework. They anticipated this design could enhance thermodynamic stability and block kinetic polymerization interactions.
When the researchers chemically excited the tetrabenzo-Chichibabin's hydrocarbon to an open-shell system, they saw that the radical centers remained active for an unusually long time—two full days—before returning to the low-energy ground state. Using a combination of high-resolution spectroscopy and theoretical calculations, the team discovered the radical's benzene rings were oriented at right angles to one another, while the ground-state compound had a relatively flat, butterfly-like ring layout. The large energy barrier between these two geometries kept the radical active. "This opens the possibility of accessing each form of the PAH molecule and understanding its physical properties," says Wu.
The researchers also modified the tetrabenzo-Chichibabin's hydrocarbon with aromatic fluorenyl rings that have well-known radical stabilizing effects. In fact, the stabilizing capacity of this compound proved so strong that the open-shell radical became the lowest-energy state, and the molecule remained stable for months under ambient air and light conditions.
Experiments revealed these new open-shell PAHs to have valuable properties including enhanced two-photon absorption, a strong magnetic response and multiple redox states. Wu notes that these findings may lead to the development of better photodynamic therapies and magnetic imaging techniques in the future.
More information: Zeng, Z., Sung, Y. M., Bao, N., Tan, D., Lee, R. et al. Stable tetrabenzo-Chichibabin's hydrocarbons: Tunable ground state and unusual transition between their closed-shell and open-shell resonance forms. Journal of the American Chemical Society 134, 14513–14525 (2012). dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja3050579
Journal information: Journal of the American Chemical Society