Stress gives cells a 'second childhood'
What doesn't kill cells may make them stronger—or considerably more flexible, at least. New findings from Haruko Obokata of the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology in Kobe and Charles Vacanti at Brigham and Women's Hospital in the United States suggest that exposing mouse cells to acidic stress can make them regress to an extremely developmentally immature state, transcending even that of embryonic stem (ES) cells.
ES cells have the developmental capacity to form any tissue type in the body and this 'pluripotency' makes them of great interest to both scientists and clinicians. As these cells must be harvested from early-stage embryos, however, human ES cell research remains a politically and ethically fraught issue. As an alternative, researchers can 'reprogram' adult cells into ES cell-like induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, which offer the advantage of being genetically matched to their donor—an important consideration for regenerative medicine. However, the generation of iPS cells typically requires the introduction of reprogramming genes, which may affect their function or risk of cancerous transformation.
Obokata and colleagues have now discovered an alternative route to pluripotency, drawing on inspiration from the plant world. "Plants [such as] carrots can produce stem cells from totally differentiated cells when they are exposed to strong external stresses like dissection," Obokata said in a recent interview with Nature. "I instinctively felt that we may have a similar mechanism to plants." To test this hypothesis, she and her colleagues isolated white blood cells from newborn mice and examined how they responded to diverse external stresses.
Back to the beginning
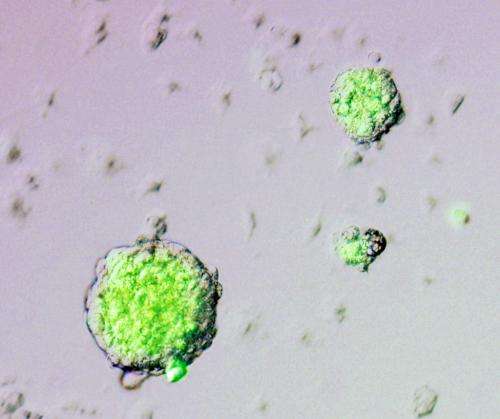
The researchers genetically modified mouse cells so that they would express a fluorescent label when Oct4, a gene prominently associated with pluripotency, was activated. Using this indicator, Obokata and colleagues determined that less than 30 minutes of exposure to acidic conditions was sufficient to spur the formation of clusters of Oct4-expressing cells (Fig. 1). Although the treatment killed most of the initial cell population, around half of the cells that survived were fluorescently labeled after a week of culture in media favorable for stem cell growth.
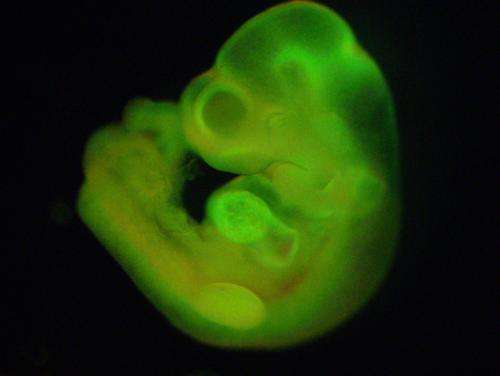
The surviving cells showed many characteristics of ES cells, including the capacity to form all of the various 'germ layers'—three distinct types of embryonic tissue that form early in development, each giving rise to a different subset of cell types. Furthermore, when these 'stimulus-triggered acquisition of pluripotency' (STAP) cells were injected into early-stage mouse embryos, they were incorporated into every tissue in the body (Fig. 2) and the embryos subsequently developed into healthy, fertile mice.
Unlike ES cells, however, the STAP cells grew poorly in culture. In an effort to bolster their proliferation, Obokata and colleagues grew the cells in stem-cell-culture medium supplemented with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a molecule that promotes ES cell growth. The cells flourished, while apparently retaining their capacity to thoroughly integrate into developing embryos. The researchers termed these more culture-friendly cells 'STAP stem cells'.
The STAP cells also had other surprises in store for the researchers. Developing embryos are surrounded by a 'support tissue' known as the trophoblast, which ultimately forms the placenta. When ES cells are transplanted into an early-stage embryo, they are generally incorporated exclusively into the embryo and not into the trophoblast. In contrast, transplanted STAP cells were integrated into both the embryo and the trophoblast. Obokata and colleagues observed that STAP cells express several genes whose activity is normally associated with the trophoblast lineage. Cultivating STAP cells in the presence of the signaling protein fibroblast growth factor (FGF) increased their similarity to trophoblast stem cells, indicating that the treatment may push the STAP cells further along in a particular developmental path. Conversely, transplanted STAP stem cells were incapable of becoming incorporated into the trophoblast and thus appear to be on a set path of embryonic tissue development.
A developing mystery
These remarkable results suggest that STAP cells may represent an even earlier stage of development than ES cells—a precursor with a capacity for pluripotency that enables differentiation into both embryonic and placental tissues. Alternatively, STAP cells may either exist in a dynamic state that shifts back and forth between the two potential developmental paths or contain separate subpopulations predisposed toward embryonic or placental differentiation. Further research will be necessary to resolve these questions.
Many other questions also remain. Obokata and colleagues successfully derived STAP cells from a wide range of source tissues in week-old mice, but it is unclear whether cells harvested from older or adult animals would retain the same capacity for pH-induced reprogramming, or whether the same protocol would work for human cells. The evolutionary advantage of having such a reprogramming pathway is also uncertain. "Why do somatic cells latently possess this self-driven ability for nuclear reprogramming?" asks Obokata. "And how is this reprogramming mechanism normally suppressed?" Resolving these questions and piecing together the events that transpire in the cellular interior during STAP reprogramming will be a top priority for her team moving forward.
In the meantime, the remarkable properties demonstrated by STAP cells and STAP stem cells suggest that they could offer an unexpectedly simple and unobtrusive mechanism by which researchers can generate pluripotent cells for research—and perhaps even clinical—applications that previously required the laborious isolation of ES or iPS cells. "It's exciting to think about the new possibilities these findings open up, not only in areas like regenerative medicine, but perhaps in the study of cellular senescence and cancer as well," says Obokata.
More information: Obokata, H., Wakayama, T., Sasai, Y., Kojima, K., Vacanti, M. P., Niwa, H., Yamato, M. & Vacanti, C. A. "Stimulus-triggered fate conversion of somatic cells into pluripotency." Nature 505, 641–647 (2014). dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12968
Obokata, H., Sasai, Y., Niwa, H., Kadota, M., Andrabi, M., Takata, N., Tokoro, M., Terashita, Y., Yonemura, S., Vacanti, C. A. & Wakayama, T. " Bidirectional developmental potential in reprogrammed cells with acquired pluripotency." Nature 505, 676–680 (2014). dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12969
Journal information: Nature
Provided by RIKEN