This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Understanding soil carbon's sensitivity to increasing global temperatures
Particulate soil carbon may be more vulnerable to microbial decomposition under warmer temperatures associated with climate change.
Soil organic matter contains more carbon than plants and the atmosphere combined. Soil is increasingly considered for its potential role in climate mitigation due to its ability to sequester more carbon, but it is also critical to understand the vulnerability of soils to losing carbon as global temperatures rise.
In a recent study, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators quantified the emergent temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon in global data and Earth system models. The research appears in Nature Geoscience.
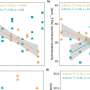
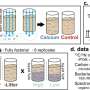
To understand the effects of temperature on soil carbon, the research considered two distinct pools of carbon in the soil: mineral-associated and particulate soil carbon. Mineral-associated carbon consists of organic compounds that are bound to the surfaces of clay minerals and can persist for hundreds of years, while particulate carbon consists of partially decomposed plant fragments that often cycle on annual to decadal timescales.
By analyzing global data on mineral-associated and particulate carbon, the team found that the climatological temperature sensitivity of particulate carbon is nearly 30% higher than that of mineral-associated carbon and more than 50% higher in cooler climates.
"We show how the temperature sensitivities of these two pools differ, which can give us insights about their relative vulnerabilities under climate change," said LLNL scientist Katerina Georgiou, lead author of the paper.
The authors show that mineral-associated soil carbon constitutes nearly 70% of the total soil carbon globally and was the major driver of its emergent temperature sensitivity. However, Earth system models vary drastically in their distribution of carbon between underlying soil pools. For instance, the global proportion of soil carbon that is conceptually similar to mineral-associated carbon varies from 16–85% across the models.
"We found that half of the Earth system models underestimate the proportion of carbon in slower cycling, mineral-protected pools, with implications for soil carbon ages and ecosystem responsiveness," Georgiou said. "The mismatch we find between the global data and Earth system models can be used to inform future model improvements."
More information: Katerina Georgiou et al, Emergent temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon driven by mineral associations, Nature Geoscience (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-024-01384-7
Provided by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory