Toward reducing the greenhouse gas emissions of the Internet and telecommunications
Amid growing concern over the surprisingly large amount of greenhouse gas produced by the Internet and other telecommunications activities, researchers are reporting new models of emissions and energy consumption that could help reduce their carbon footprint. Their report appears in ACS' journal Environmental Science & Technology.
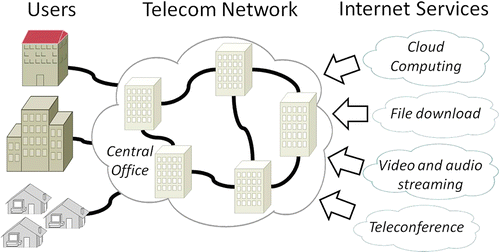
Researchers from the Centre for Energy-Efficient Telecommunications (CEET) and Bell Labs explain that the information communications and technology (ICT) industry, which delivers Internet, video, voice and other cloud services, produces more than 830 million tons of carbon dioxide (CO2), the main greenhouse gas, annually. That's about 2 percent of global CO2 emissions—the same proportion as the aviation industry produces. Projections suggest that ICT sector's share is expected to double by 2020. The team notes that controlling those emissions requires more accurate but still feasible models, which take into account the data traffic, energy use and CO2 production in networks and other elements of the ICT industry. Existing assessment models are inaccurate, so they set out to develop new approaches that better account for variations in equipment and other factors in the ICT industry.
They describe development and testing of two new models that better estimate the energy consumption and CO2 emissions of Internet and telecommunications services. They tested the models on a simulated network and on a deployed network that serves the majority of schools in California. Both models delivered better estimates than the current "top-down" models. The researchers suggest, based on their models, that more efficient power usage of facilities, more efficient use of energy-efficient equipment and renewable energy sources are three keys to reducing ICT emissions of CO2.
CEET is a partnership between Alcatel-Lucent, the University of Melbourne and the Victorian State Government. It is the world's first research center exclusively dedicated to energy-efficient telecommunications technologies. Its research efforts cover a broad range of telecommunications network infrastructures and how those elements can increase their energy efficiency.
More information: Methodologies for Assessing the Use-Phase Power Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Telecommunications Network Services, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47 (1), pp 485–492. DOI: 10.1021/es303384y
Abstract
Internet traffic has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to continue to expand significantly over the next decade. Consequently, the resulting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of telecommunications service-supporting infrastructures have become an important issue. In this study, we develop a set of models for assessing the use-phase power consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of telecom network services to help telecom providers gain a better understanding of the GHG emissions associated with the energy required for their networks and services. Due to the fact that measuring the power consumption and traffic in a telecom network is a challenging task, these models utilize different granularities of available network information. As the granularity of the network measurement information decreases, the corresponding models have the potential to produce larger estimation errors. Therefore, we examine the accuracy of these models under various network scenarios using two approaches: (i) a sensitivity analysis through simulations and (ii) a case study of a deployed network. Both approaches show that the accuracy of the models depends on the network size, the total amount of network service traffic (i.e., for the service under assessment), and the number of network nodes used to process the service.
Journal information: Environmental Science & Technology
Provided by American Chemical Society
















