Using magnetic fields to control newly identified state of matter could enable more efficient memory devices

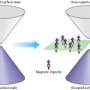
Scientists in Japan have shown that the properties of a recently discovered state of matter—a chiral spin liquid—can be controlled by applying a magnetic field1, a concept that could be harnessed for low-energy-consumption memory devices .
Many ferromagnetic materials exhibit the so-called ‘anomalous Hall effect’ (AHE), whereby the electrons flowing through the materials experience a lateral force pushing them to one side as a result of the materials’ intrinsic magnetization. In materials exhibiting the ‘conventional’ Hall effect, the lateral force is caused by an external magnetic field. The magnetic material Pr2Ir2O7 is a special case because it displays AHE without possessing a uniform magnetization. This unusual behavior was recently recognized and analyzed for the first time by Shigeki Onoda from the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, Wako, and his colleagues2. They interpreted this behavior as a good indication that Pr2Ir2O7 exists as a chiral spin liquid in which effects such as AHE depend on which direction an electron is travelling.
The collaboration team of the theoretical physicist, Onoda, and colleagues at The University of Tokyo and the Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, and Florida State University, USA, discovered they could control this enigmatic material by experimentally investigating how the AHE in Pr2Ir2O7 depends on applied-magnetic-field strength at temperatures below 2 kelvin. They found that the sign of the voltage drop associated with the anomalous Hall effect can be reversed by a sweep cycle of a magnetic field without causing an effect called hysteresis—where the magnetization depends on the direction in which the magnetic field is swept. “Magnetization hysteresis is a main cause of heat or energy loss,” explains Onoda. “Thus, our results prove that this material could function as a nonvolatile memory device.”
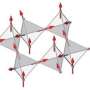
These properties arise because every physical system organizes in a way that minimizes its energy. In some materials, two competing influences—the arrangement of the crystal lattice and the ordering of local magnetic moments or ‘spins’ of electrons—cannot balance because they cannot simultaneously attain their minimum energy state. Known as geometric frustration, this situation prevents the system from settling in a particular state, and means that the spins fail to become ordered even at absolute zero. For this reason, physicists called these materials spin liquids.
“To practically harness the effects of AHE in a chiral spin liquid, the chirality must remain finite at room temperature,” says Onoda. Although a difficult challenge, the current work is a positive start.
More information: Balicas, L., et al. Anisotropic hysteretic Hall effect and magnetic control of chiral domains in the chiral spin states of Pr2Ir2O7. Physical Review Letters 106, 217204 (2011).
Provided by RIKEN