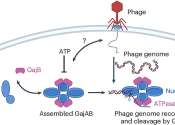
Study details a common bacterial defense against viral infection
One of the many secrets to bacteria's success is their ability to defend themselves from viruses, called phages, that infect bacteria and use their cellular machinery to make copies of themselves.