Last update:
Soft Matter news

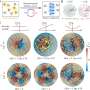
Scientists achieve unprecedented control of active matter
An international research team led by Brandeis University has achieved a major breakthrough in the field of active matter physics, as detailed in a study published this week in Physical Review X. This pioneering research ...
Soft Matter
Oct 4, 2024
0
138

Ocean waves grow way beyond known limits, new research finds
Scientists have discovered that ocean waves may become far more extreme and complex than previously imagined.
General Physics
Sep 18, 2024
5
264

Beneath the brushstrokes, van Gogh's sky is alive with real-world physics
Vincent van Gogh's painting "The Starry Night" depicts a swirling blue sky with yellow moon and stars. The sky is an explosion of colors and shapes, each star encapsulated in ripples of yellow, gleaming with light like reflections ...
Soft Matter
Sep 17, 2024
0
66

Science fair project leads to new research explaining the glugging effect
As Rohit Velankar, now a senior at Fox Chapel Area High School, poured juice into a glass, he could feel that the rhythmic "glug, glug, glug" was flexing the walls of the carton.
General Physics
Sep 10, 2024
0
52

Researchers make sound waves travel in one direction only, with implications for electromagnetic wave technology
Researchers at ETH Zurich have managed to make sound waves travel only in one direction. In the future, this method could also be used in technical applications with electromagnetic waves.
General Physics
Sep 6, 2024
0
813

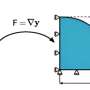
Discovery of a new convective instability in complex fluids, 140 years after Lord Rayleigh
An altogether new convective instability has been predicted and experimentally discovered, 140 years after Lord Rayleigh. Convective instabilities are of fundamental importance for both our everyday life as well as for ecology ...

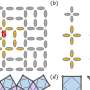
Langbeinites show talents as 3D quantum spin liquids
A 3D quantum spin liquid has been discovered in the vicinity of a member of the langbeinite family. The material's specific crystalline structure and the resulting magnetic interactions induce an unusual behavior that can ...
Soft Matter
Aug 23, 2024
0
191

Physicists develop new model that describes how filaments assemble into active foams
Many fundamental processes of life, and their synthetic counterparts in nanotechnology, are based on the autonomous assembly of individual particles into complex patterns. LMU physicist Professor Erwin Frey, Chair of Statistical ...
General Physics
Aug 21, 2024
0
9

Scientists characterize shale cap rocks at tiny scales
A team of researchers is working on a multidisciplinary approach to advancing the exploration of shale rock as a suitable geological seal for resource recovery and underground storage. Given that the pore space in shale rock ...
General Physics
Aug 15, 2024
0
4

Cricket physics: Wind tunnel experiments reveal why bowling with a near horizontal arm makes for tough batting
Key to winning a cricket match is tricking the other team's batters—no small feat, as bowlers bowl cricket balls nearly 100 miles per hour. In recent years, a bowling technique that has become popular involves keeping the ...
General Physics
Aug 13, 2024
0
0

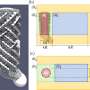
A new robotic platform to reproduce and study complex ciliary behavior
Cilia are sensory structures extending from the surface of some cells. These hair-like structures are known to contribute to the sensorimotor capabilities of various living organisms, including humans.

High-speed cameras reveal behavior of microplastics in turbulent water
Microplastics are a global problem: they end up in rivers and oceans, they accumulate in living organisms and disrupt entire ecosystems. How tiny particles behave in a current is difficult to describe scientifically, especially ...
General Physics
Aug 12, 2024
0
67

Ability to track nanoscale flow in soft matter could prove pivotal discovery
For roughly 70 years, Play-Doh has been entertaining children with its moldable, squishy form. This familiar substance belongs to a broader category known as soft matter, which includes some foods (such as mayonnaise), 3D ...
Soft Matter
Aug 9, 2024
0
57

New self-powered electrostatic tweezer enhances object manipulation and microfluidics
In a study published in Device has reported a new self-powered electrostatic tweezer that offers superior accumulation and tunability of triboelectric charges, enabling unprecedented flexibility and adaptability for manipulating ...
Soft Matter
Jul 26, 2024
0
102

Team develops novel hybrid scheme for compressible flow computations
A team of scientists has developed a novel hybrid scheme for both steady and unsteady single-phase compressible flow simulations. Their scheme has potential applications in real-world scenarios, offering a promising avenue ...
Soft Matter
Jul 26, 2024
0
93

Exploring what happens when different spherical objects hit the water
When an object hits a body of water vertically, it is accompanied by a strong hydrodynamic force fueled by the flow of water around it, which propels it forward. The magnitude of this force is known to vary depending on the ...

Study finds active matter and shear flows share thinning behaviors
According to a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a research team led by Professor Xu Ning from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has found that active matter and shear ...
Soft Matter
Jul 24, 2024
0
132

Does heat travel differently in tight spaces? New insights into convection heat and fluid mechanics
A search for "air fryer recipe" on most social media platforms likely returns a flood of food videos touting quick and easy meal ideas. The market touts these devices as a convenient, clean, quick way to heat and crispen ...
General Physics
Jul 24, 2024
0
33

Study shows elephant trunk dexterity can be mimicked with minimal actuators
The trunk of an elephant is among the versatile appendages in the animal kingdom. Now a research team has shown that most of its dexterity can be reproduced with a model using just three "muscles." And they built a physical ...

Two-in-one mapping of temperature and flow around microscale convective plumes
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised a way to measure both the temperature and velocity profiles of fluid in a convective plume at millimeter length scales in 3D. They combined near-infrared absorption ...
General Physics
Jul 22, 2024
0
7
More news

Modeling a right royal butterfly effect

Model shows how plankton survive in a turbulent world

Study sheds light on the origin of elasticity in glasses and gels
Other news

Bat data study reveals conservation priorities in San Diego County

Targeting 'undruggable' diseases: Researchers reveal new levels of detail in targeted protein degradation

'Party atmosphere': Skygazers treated to another aurora show

Scientists discover how innate immunity envelops bacteria

Machine learning could improve extreme weather warnings
Toward a unified theory for dynamics of glassy materials

Intelligent liquid: Researchers develop metafluid with programmable response
Understanding flow and sound through large-scale computations
Breaking the ice: Molecular insights into saltwater droplet freezing

Gazing at your dog can connect your brains, research suggests
Oxidative stress: How protein recycling protects against cell death

Intra-molecular distances in biomolecules measured optically with Ångström precision