This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Novel strategy proposed for selectively targeting G-quadruplex at specific genome loci
DNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) are a type of quadruple helix structure formed by a continuous guanine-rich DNA sequence. Although DNA G4s are thought to be involved in various biological processes, in many cases their causative effects are largely unclear due to lack of suitable strategies for selectively stabilizing DNA G4 at specific loci.
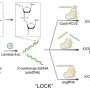
In a study published in Nature Cell Biology on July 3, Prof. Qu Xiaogang from the Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry (CIAC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and his colleagues presented a novel strategy to achieve DNA G4s stabilization at specific genome loci by combining the CRISPR and G4-stabilizing proteins or compounds.
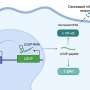
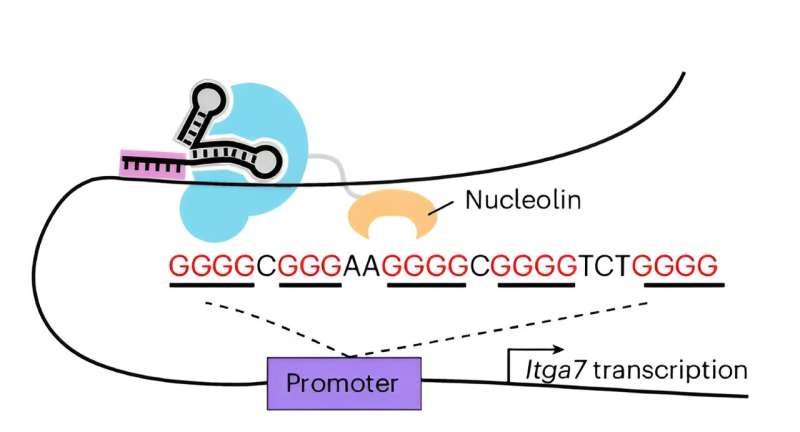
The researchers employed clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated dead Cas9 (CRISPR/dCas9) targeting constructs to endow G4-stabilizing molecules with selectivity among different G4s. And the dCas9/G4-stabilizing molecules complexes can stabilize any G4 structure in the genome by strategic single-guide RNA (sgRNA) design without a significant effect of other non-targeted G4 in live cells.
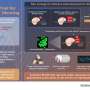
The fusion of G4-stabilizing protein nucleolin with dCas9 can specifically stabilize G4s in the promoter of oncogene MYC and muscle associated gene Igta as well as telomere G4s, leading to cell proliferation arrest, inhibition of myoblast differentiation and cell senescence, respectively.
In addition, CRISPR can confer intra-G4 selectivity to G4-binding compounds pyridodicarboxamide (PDC) and pyridostatin (PDS). This strategy has been used to stabilize the G4s within the promoter regions of two well-established lncRNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1, as well as several key genes implicated in ferroptosis, oxidative stress, hypoxia response, and MAPK pathway.
Compared with traditional G4 ligands, CRISPR-guided biotin-conjugated PDC and PDS enable a more precise investigation into the biological functionality of de novo G4s.
This strategy would pave the way for illustrating the association of specific G4s with defined biological processes or human diseases. Additionally, it may open a new avenue in live cells for screening of G4 probe or G4 drug candidate, which possesses specific targeting only to the interested G4 with the low risk of off-target effects, promoting G4-based disease diagnosis and therapy.
More information: Geng Qin et al, Targeting specific DNA G-quadruplexes with CRISPR-guided G-quadruplex-binding proteins and ligands, Nature Cell Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01448-1
Journal information: Nature Cell Biology
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences