This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
CRISPRlnc: New lncRNA-specific SgRNA design method proposed
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are non-protein-coding transcripts. Currently, CRISPR/Cas9 is a promising RNA-guided genome editing technology consisting of a Cas9 nuclease and a single-guide RNA (sgRNA). Considering the significant differences between lncRNAs and protein-coding genes, it is necessary to investigate sgRNA design method optimized for lncRNAs.
Researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) studied the application of CRISPR/Cas9 technology in gene editing, especially for sgRNA design against long noncoding RNA (lncRNA).
They first evaluated the performance of a series of known sgRNA design tools on coding and noncoding datasets and analyzed the different performances in terms of sgRNA specificity to lncRNA, including nucleic acid sequence, genomic location, and editing mechanism preference. Results were published in Briefings in Bioinformatics.
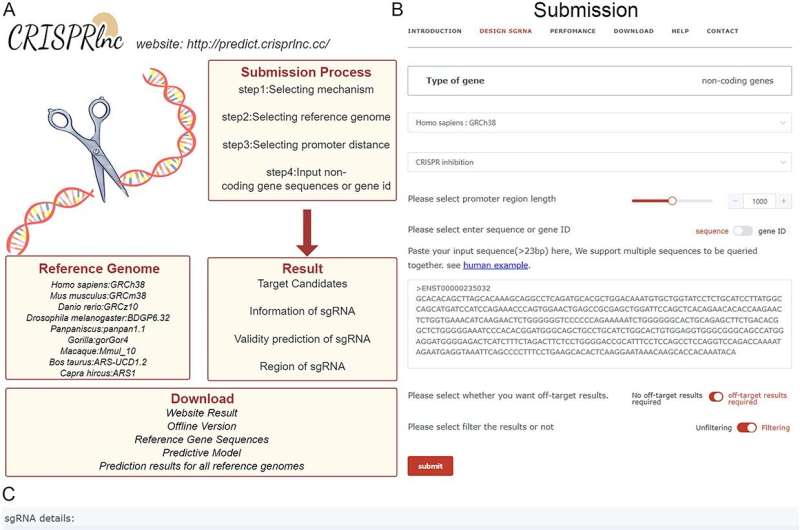
The researchers also introduced a support vector machine-based machine learning algorithm, CRISPRlnc, which aims to simulate the CRISPR knockout (CRISPRko) and CRISPR inhibition (CRISPRi) mechanisms to predict the targeting activity of the target. CRISPRlnc combines paired sgRNA design and off-target analysis to achieve one-stop design of CRISPR/Cas9 sgRNA for noncoding genes.
By comparing the performance of CRISPRlnc with several existing methods on multiple datasets, the researchers conclude that CRISPRlnc performs much better than existing methods for lncRNA-specific sgRNA design for both CRISPRko and CRISPRi mechanisms.
"We have proposed a new machine learning method, CRISPRlnc, for the design of lncRNA-specific sgRNA in the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The performance comparison shows that CRISPRlnc is far superior to existing methods for lncRNA-specific sgRNA design in both CRISPRko and CRISPRi mechanisms," said Liu Changning of XTBG.
To facilitate the use of CRISPRlnc, the researchers developed a web server and made it available for download on GitHub. For the convenience of users, they integrate services such as paired sgRNA design and off-target risk analysis into the implementation of the CRISPRlnc tool, and provide a variety of information such as on-target validity, off-target risk and genomic location to help further select sgRNAs.
More information: Zitian Yang et al, CRISPRlnc: a machine learning method for lncRNA-specific single-guide RNA design of CRISPR/Cas9 system, Briefings in Bioinformatics (2024). DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbae066
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences