This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study reveals historical mismatch in Southern Ocean contributes to heat and carbon uptake
The Southern Ocean plays a central role in the global uptake of heat and carbon, which is widely thought to be due to its unique upwelling and circulation. An international research team, led by the University of Liverpool, explored whether there are differences in how the Southern Ocean contributes to the global uptake of heat and carbon.
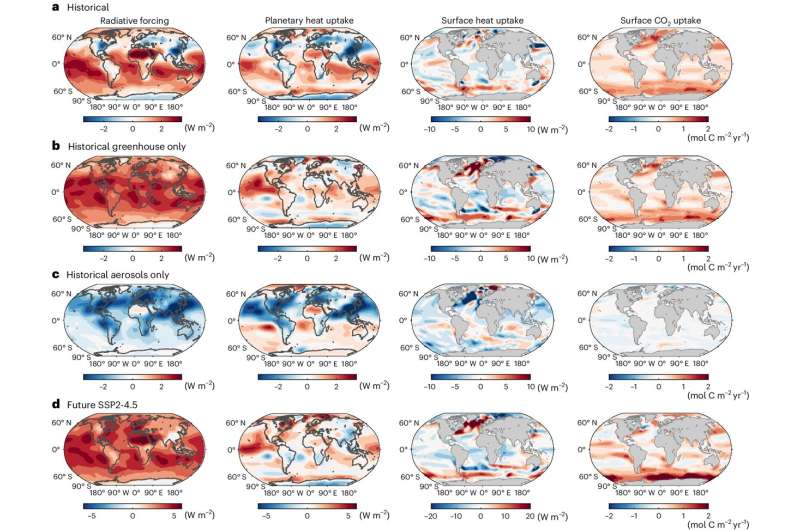
Their findings, published in the journal Nature Climate Change, show that for the period from 1861 to 2005, the Southern Ocean contributed nearly twice as much to the global ocean uptake of heat compared to the global uptake of carbon.
Their analysis of state-of-the-art models of carbon and heat uptake across global oceans covering this period revealed large differences in uptake, with the Southern Ocean accounting for 83% of global ocean heat uptake and 43% of global ocean carbon uptake.
Further analysis using single-radiative forcing experiments indicated that this contrast between hemispheres in heat uptake was due to aerosol forcing, which is predominantly found over the northern hemisphere and caused a reduction in the uptake of heat by the northern oceans.
Aerosol forcing—or aerosol particles such as dust, haze or smoke—acts as a barrier to reflect sunlight and counter the effect of extra heating from rising atmospheric carbon that then impacts the uptake of heat by northern oceans.
However, the study revealed that the historical hemispheric contrast does not apply to the carbon cycle, with atmospheric carbon increasing in a broadly similar manner over both hemispheres.
Looking to the future, the study projects that where greenhouse gases increasingly dominate radiative forcing, the northern oceans' heat uptake will increase more in line with the northern oceans' carbon uptake. Thus, the Southern Ocean's contributions to global heat and carbon uptake will become more comparable in the future.
Professor Ric Williams, from the University of Liverpool and lead author of the paper, said, "While there are unique upwelling and overturning circulations occurring in the Southern Ocean, our analysis suggests that the primary reason for the enhanced Southern Ocean uptake of heat relative to carbon are differences in their atmospheric sources.
"Over the historical period, there are strong contrasts in radiative forcing between the southern and northern hemispheres with aerosol forcing providing a cooling over much of the northern hemisphere.
"What is really interesting is that when you look to the future, we see a different response: the greenhouse gas forcing is expected to dominate more than the aerosol forcing, so that there is less hemispheric contrast in the radiative forcing. Hence, the future response may be different to the past."
Dr. Andrew Meijers, leader of the British Antarctic Survey Polar Oceans group, and co-author of the study, said, "This study shows how aerosol pollution has been shielding the northern oceans from warming over the last century or so. It also demonstrates the worrying potential for dramatically increased ocean heating, particularly in the North Atlantic, in the coming decades as aerosol emissions are reduced, and CO2 warming begins to dominate."
More information: Richard G. Williams et al, Asymmetries in the Southern Ocean contribution to global heat and carbon uptake, Nature Climate Change (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41558-024-02066-3
Journal information: Nature Climate Change
Provided by University of Liverpool