This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
After the Ice Age, people returned to the Swabian Jura 3,000 years earlier than previously thought

A new study shows that parts of central Europe were repopulated some 3,000 years earlier than previously thought following the inhospitable conditions of the last ice age.
The ice age lasted from around 27,000 to 19,000 years ago. Archaeologists long believed that people returned to the Swabian Jura region in what is now southern Germany about 16,500 years ago. New data from two sites in the Lone Valley now shows that modern humans left traces of habitation there around 19,500 years ago.
The study is by Benjamin Schürch, Dr. Gillian Wong and Dr. Elisa Luzi from the University of Tübingen and Professor Nicholas Conard, who is additionally a member of the Senckenberg Center for Human Evolution and Paleoenvironment.
The research team also used additional findings from the Vogelherd cave and the Langmahdhalde site to trace the recolonization more precisely in terms of space and time. The study has been published in the latest edition of Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
Vogelherd cave was first excavated in 1931 by Gustav Riek from the University of Tübingen. The work had to be completed within a short period of time; as a result, the layers were not systematically documented. Later excavations, including re-examination of the overburden from the 1931 dig, were carried out by Nicholas Conard and his team.
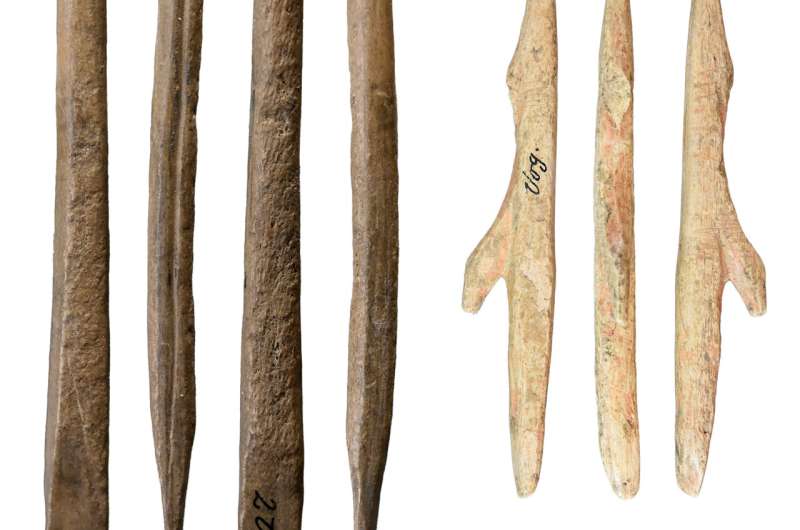
"The site is primarily known for its small figurines from the Aurignacian culture, which was prevalent around 42,000 to 35,000 years ago," says Benjamin Schürch. "But there are also traces of the Magdalenian period, an archaeological cultural stage around 19,000 to 14,000 years ago with stone tools used for working hide and antler, as well as spearheads made of antler."
The Langmahdhalde rock shelter is only about 2 kilometers away from the Vogelherd Cave. This site was excavated from 2016 to 2024 under the direction of Conard; the layers were meticulously documented.

Dating of organic matter
The research team radiocarbon dated animal remains from the Vogelherd cave that were worked by humans, as well as organic material from the Langmahdhalde site that was found in direct association with Magdalenian stone tools.
This method makes use of the fact that organically bound carbon-14 decomposes at a rate which can be precisely calculated. Its proportion in organic samples therefore provides information about the age of the artifacts sampled.
"The oldest of these traces left by humans were dated to around 19,500 years ago in the Vogelherd cave. At the Langmahdhalde site, people appear to have stayed for the first time after the Ice Age between 17,900 and 17,000 years ago," Schürch explains.
At each of the excavation sites, the researchers carefully analyzed the cultural remains in the vicinity of the dated finds. For example, they used spear heads made of antler and stone from the Magdalenian period of the Vogelherd cave. By analyzing the microfauna remains at the Langmahdhalde, the researchers were also able to draw important conclusions about the climate in the region around 19,000 years ago.
"As the sites are so close together geographically, we were able to correlate the more extensive finds from the Vogelherd with the more precisely documented sequence of layers at the Langmahdhalde. This was the only way we could gain a more comprehensive picture," says Gillian Wong.
She says that although modern humans had repopulated the Swabian Jura in isolated cases at the end of the Ice Age, "they only settled permanently in the region again around 16,500 years ago."
More information: Benjamin Schürch et al, Evidence for an earlier Magdalenian presence in the Lone Valley of southwest Germany, Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104632
Journal information: Journal of Archaeological Science
Provided by Universitaet Tübingen