This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Green hydrogen: 'Artificial leaf' becomes better under pressure

Hydrogen can be produced via the electrolytic splitting of water. One option here is the use of photoelectrodes that convert sunlight into voltage for electrolysis in so-called photoelectrochemical cells (PEC cells). A research team at HZB has now shown that the efficiency of PEC cells can be significantly increased under pressure.
Some call it an 'artificial leaf': instead of the natural Photosystem II complex that green leaves in nature use to split water with sunlight, photoelectrochemical cells, or PEC cells for short, use artificial, inorganic photoelectrodes to generate the voltage required for the electrolytic splitting of water from sunlight.
Minimizing losses
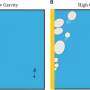
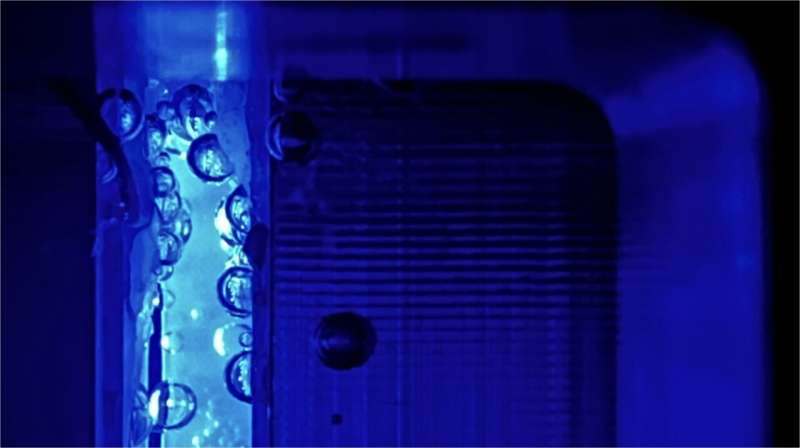
The best performing devices already achieve impressive energy conversion efficiencies of up to 19%. At such high efficiencies, losses due to bubble formation start to play an important role. This is because bubbles scatter light, preventing optimal illumination of the electrode.
Moreover, bubbles may block the electrolyte from contacting the electrode surface and thus cause electrochemical deactivation. To minimize these losses, it would help to reduce the bubble sizes by operating the device at higher pressure. However, all PEC devices reported thus far have been operating at atmospheric pressure (1 bar).
Enhancing the pressure
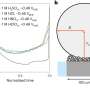
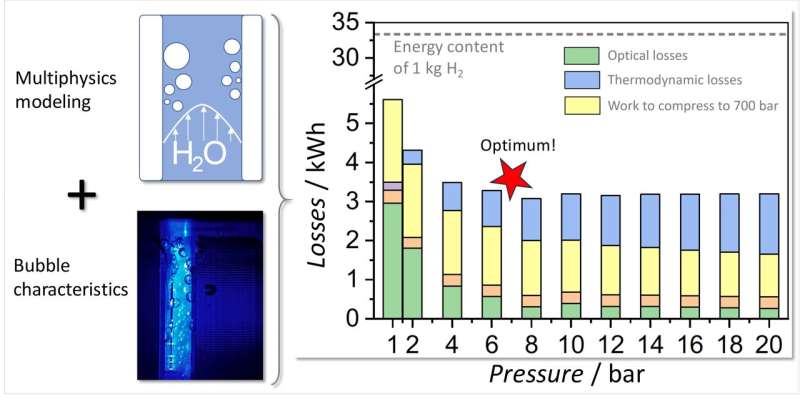
A team from the Institute for Solar Fuels at HZB has now investigated water splitting at elevated pressure under PEC-relevant conditions. They used gas to pressurize PEC flow cells to between 1 and 10 bar and recorded a number of different parameters during electrolysis. They also developed a multiphysics model of the PEC process and compared it with experimental data at normal and elevated pressure.
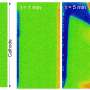
This model now allows to play with the parameters and identify the key levers. "For example, we investigated how the operating pressure affects the size of the gas bubbles and their behavior at the electrodes," says Dr. Feng Liang, first author of the paper now published in Nature Communications.
Energy losses halved
The analysis shows that increasing the operating pressure to 8 bar halves the total energy loss, which could lead to a relative increase of 5–10% in the overall efficiency.
"The optical scattering losses can be almost completely avoided at this pressure," explains Liang. "We also saw a significant reduction in product cross-over, especially the transfer of oxygen to the counter electrode".
At higher pressures, however, there is no advantage, so the team suggests 6–8 bar as the optimum operating pressure range for PEC electrolyzers.
"These findings, and in particular the multiphysics model, can be extended to other systems and will help us to increase the efficiencies of both electrochemical and photocatalytic devices," says Prof. Dr. Roel van de Krol, who heads the Institute for Solar Fuels at HZB.
More information: Feng Liang et al, Assessing elevated pressure impact on photoelectrochemical water splitting via multiphysics modeling, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49273-2
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres