This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Unveiling crucial virulent milRNAs implicated in the initial infection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense
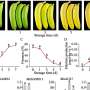
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is a typical soil-borne fungus that causes Fusarium wilt by infecting the roots and blocking the vascular tissues of host banana plants, and threatens global banana production. In total, four races have been reported in Foc, of which the tropical race 4 (TR4) is the most widespread race.
In some severely affected banana plantations, the conventional Cavendish variety had to be abandoned for other alternative crops due to the spread of TR4. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of FWB and the development of improved control methods is urgently needed.
New research addressing this topic is published in the journal Mycology.
A growing number of milRNAs have been recognized for their roles in fungal growth, development and pathogenicity. Little is known about the role of these kinds of small RNAs produced by soil-brone fungus Foc in pathogenicity and other biological processes.
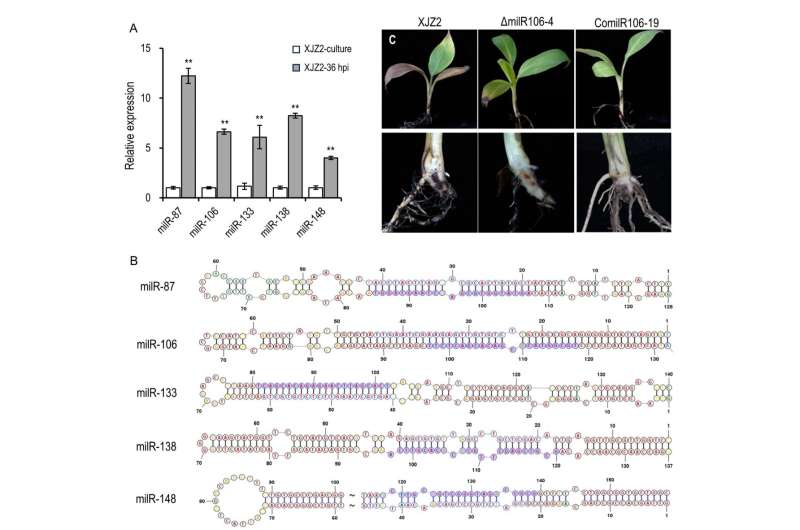
In the study, six milRNAs that are significantly induced during the early stages of Foc infection were identified using small RNA sequencing and bioinformatic analysis. Among them, milR106 stands out due to its unique dependence on the FoDCL2 gene for biosynthesis. In contrast, the production of milR87, milR133, milR138, and milR148 is influenced by both FoDCL2 and FoQDE2.
The functional analysis revealed that milR106 plays an important role in Foc virulence by regulating fungal conidiation, hydrogen peroxide sensitivity, and infective growth. Gene ontology analysis of the six milRNAs' target genes in the banana genome revealed enrichment in defense response to fungus and cellular response to hypoxia, implying the importance of these target genes in response to pathogen infection.
The discovery of these infection-induced, pathogenicity-critical milRNAs provides valuable molecular targets for the design of efficient control strategies against Fusarium wilt of bananas. By unraveling the involvement of milRNAs in Foc's virulence, this work advances our knowledge of the intricate mechanisms underlying this economically important disease and lays the groundwork for future endeavors aimed at enhancing disease resistance in banana cultivars and refining disease management practices.
More information: Lifei Xie et al, Unveiling microRNA-like small RNAs implicated in the initial infection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense through small RNA sequencing, Mycology (2024). DOI: 10.1080/21501203.2024.2345917
Provided by Tsinghua University Press