This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Satellite maps boost mangrove conservation in China
Mangroves are vital ecosystems along coastlines, providing essential services such as coastal protection, biodiversity enhancement, and carbon sequestration. Despite their critical importance, effective management of these areas is often hampered by the challenges of acquiring accurate, species-specific data.
These challenges are compounded by the mangroves' remote locations and the dynamic nature of their environments. To address this data shortfall, cutting-edge mapping technologies have been developed.
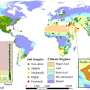
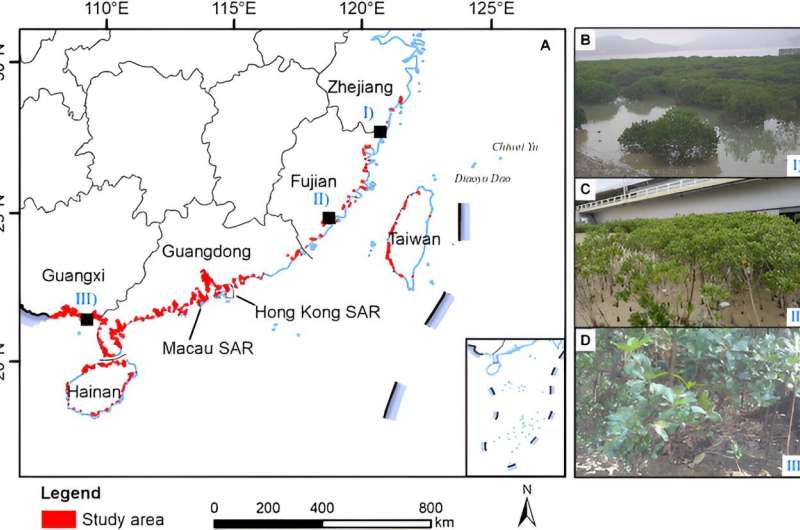
A new study, published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on April 15, 2024, employs Sentinel-2 satellite imagery to map the distribution of the mangrove species Kandelia obovata across China, significantly advancing conservation efforts.
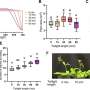
Researchers have pinpointed the phenological variations—periodic changes in the plants' life cycles across seasons. They identified specific times when the species' physical characteristics are most distinguishable from other mangroves and vegetation, such as during the senescence phase when many plants lose their leaves while K. obovata remains evergreen.
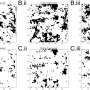
The study introduces a "dual-temporal" imaging strategy that captures the mangrove at times when it is most easily differentiated from other species and during off-peak seasons to distinguish it from surrounding salt marshes. This approach has markedly improved the precision of species-specific mapping, achieving an impressive 88.5% accuracy.
Such detailed mapping is crucial for effective conservation, enabling a better understanding of species distribution patterns, monitoring environmental changes, and managing these crucial ecosystems against environmental and anthropogenic stresses.
Dr. Mingming Jia, the lead researcher, noted, "Our research not only deepens our understanding of mangrove distribution but also directly supports the ecological restoration initiatives detailed in China's Special Action Plan for Mangrove Protection and Restoration. This technology facilitates precise, cost-effective, and extensive environmental monitoring."
The meticulous mapping of Kandelia obovata facilitates targeted conservation strategies, efficient resource allocation, and enhanced ecological impact assessments. It also provides policymakers and conservationists with a valuable dataset to track the progress of mangrove restoration and assess the effectiveness of current management practices.
More information: Chuanpeng Zhao et al, Distribution of Mangrove Species Kandelia obovata in China Using Time-series Sentinel-2 Imagery for Sustainable Mangrove Management, Journal of Remote Sensing (2024). DOI: 10.34133/remotesensing.0143
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences