This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Rice husk can be used as a promising sustainable packaging material
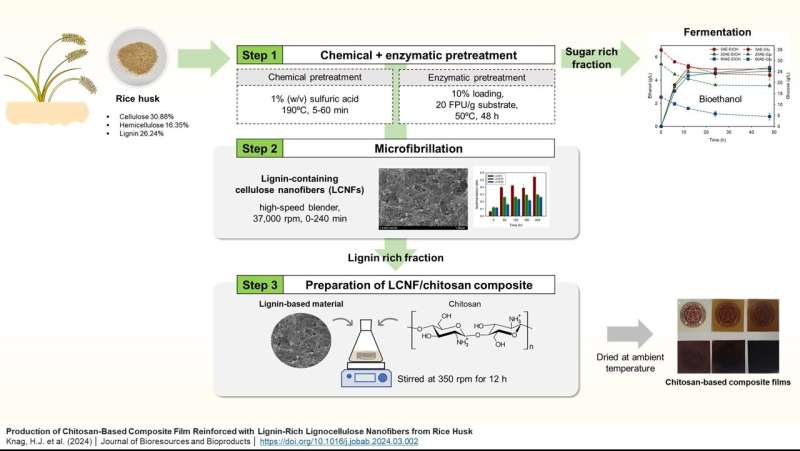
Rice husk, the hard-protective layer that envelopes the inner grain of rice, constitutes approximately 20%–25% of the entire rice structure and produces a considerable amount of by-products. In a study published in the journal, Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, researchers have unveiled a pioneering approach to creating eco-friendly chitosan-based composite films using lignin-rich lignocellulose nanofibers extracted from rice husk.
This innovative research not only addresses the pressing need for sustainable materials but also offers a promising solution to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy practices.
The production process begins with the chemical pretreatment of rice husks, followed by enzymatic hydrolysis to produce ethanol in a biorefinery platform. Even after this usual biorefinery process, the residual solid fraction could be considered as one option for the production of lignin-rich nanofibers. These nanofibers, known for their strength and hydrophobic unique properties, are then incorporated into chitosan to form composite films with enhanced mechanical performance and structural integrity.
One of the key highlights of this study is the utilization of agricultural waste, such as rice husks, as a renewable source for producing value-added materials. By repurposing waste into functional composite films, the research contributes to waste reduction and underscores the importance of sustainable resource management. The biodegradability of chitosan-based composite films aligns with the global shift towards eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, offering a greener choice for various industries.
The incorporation of lignin-rich nanofibers not only improves the strength and durability of the composite films but also imparts unique properties such as UV-blocking and mechanical properties, expanding their potential applications in food packaging, biomedical devices, and agricultural films. This versatile material opens up new possibilities for creating bio-based products that are both environmentally friendly and high-performing.
Lead researchers, Young Hoon Jung and Hye Jee Kang, from Kyungpook National University, emphasize the significance of this study in advancing sustainable material development and waste valorization. The research team's innovative approach showcases the feasibility of producing chitosan-based composite films reinforced with lignin-rich nanofibers, paving the way for a greener future in food or biomaterial industry.
More information: Hye Jee Kang et al, Production of Chitosan-Based Composite Film Reinforced with Lignin-Rich Lignocellulose Nanofibers from Rice Husk, Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jobab.2024.03.002
Provided by Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts