This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Protein fragments ID two new 'extremophile' microbes—and may help find alien life

Perfectly adapted microorganisms live in extreme environments, from deep-sea trenches to mountaintops. Learning more about how these extremophiles survive in hostile conditions could inform scientists about life on Earth and potential life on other planets.
In the Journal of Proteome Research, researchers detail a method for more accurate extremophile identification based on protein fragments instead of genetic material. The study identified two new hardy bacteria from high-altitude lakes in Chile—an environment like early Mars.
Even though humans tend to avoid settling in extremely hot, cold, or high-altitude areas, some microorganisms have adapted to live in such harsh locations. These extremophile microbes are of interest to astrobiologists who are searching for life on other planets.
Researchers currently use individual gene sequencing to identify Earth-bound microbes based on their DNA. However, current methods can't distinguish closely related species of extremophiles. So, Ralf Moeller and colleagues investigated whether they could identify an extremophile by using its protein signature rather than a gene sequence.
The researchers started their demonstration with water samples from five high-altitude Andean lakes more than 2.3 miles above sea level in the Chilean Altiplano. (For reference, Denver is about one mile above sea level.) From the samples, the researchers cultivated 66 microbes and then determined which of two methods better identified the microorganisms:
- Traditional gene sequencing compared the nucleotides of the 16s rRNA gene (a typical gene for sequence-based microbe analysis) from each sample to a database for identification.
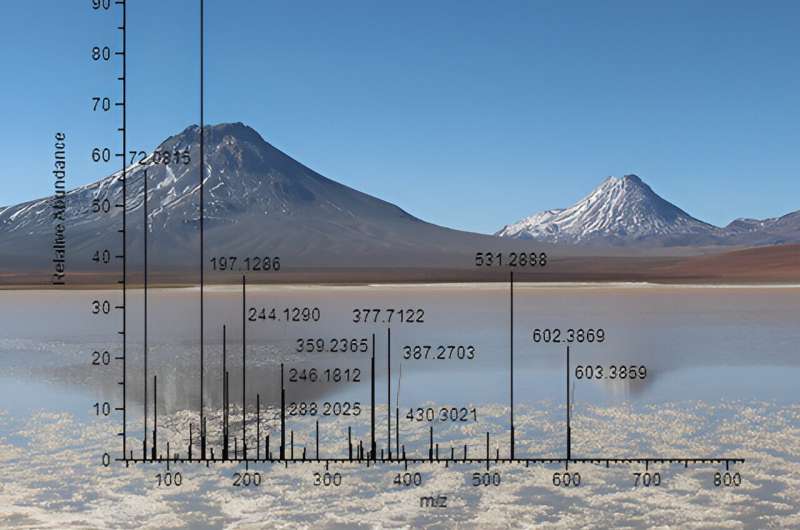
- The newer "proteotyping" technique analyzed protein fragments known as peptides to produce peptide signatures, which the team used to identify microorganisms from proteome databases.
With these methods, the researchers identified 63 of the 66 microorganisms that were cultivated from the high-altitude lake samples. For the three microorganisms that gene sequencing failed to identify because their genetic information wasn't in the available database, proteotyping identified two potentially new types of extremophile bacteria.
These results suggest proteotyping could be a more complete solution for identifying extremophile microorganisms from small biological samples. The team says protein profiling could someday help us search for and identify extraterrestrial life and better explore the biodiversity on our own planet.
More information: Katharina Runzheimer et al, Exploring Andean High-Altitude Lake Extremophiles through Advanced Proteotyping, Journal of Proteome Research (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00538
Journal information: Journal of Proteome Research
Provided by American Chemical Society