This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study analyzes how lies affect economic decisions
Psychology and Economics come together in a recent line of research, led by Ismael Rodríguez-Lara, Professor at the University of Malaga, who studies how lies affect economic decisions.
It is a study, developed together with the Professor at the University of California (Santa Barbara) Gary Charness, has analyzed the way in which morality influences the degree of lying in certain economic situations. The results of this research have been published in the scientific journal Economics Letters.
"In many economic situations such as tax filing or tax fraud, to give a few examples, it is very important to understand when, how and why people lie," says the UMA researcher.
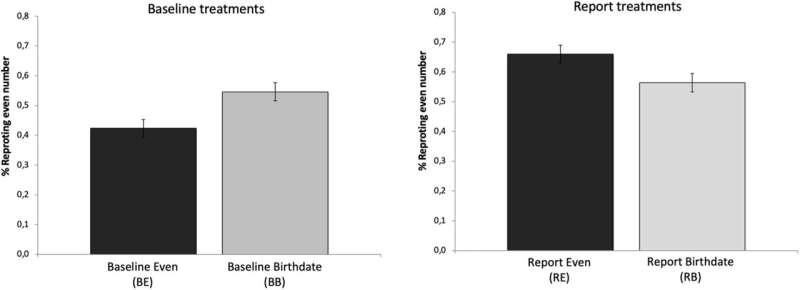
Based on experiments carried out last year in the United Kingdom, it has been shown that it is the 'moral costs', which precisely encompass non-economic aspects, that determine that people lie less. A total of one thousand people have been studied.
"The usual thing is to consider that the degree of lying is affected by economic issues, such as the benefits we obtain or the possible costs that have to be paid, in the form of fines," explains Rodriguez-Lara. However, the results obtained with this research show that morality is also important: "When the information being disclosed is personal, then people lie less than if the information is non-personal," he says.
In this sense, the Professor of the UMA explains that this is due to factors related to people's expectations not to disappoint themselves, as well as to differentiate themselves from the rest. "People feel a higher moral cost of lying when the information is personal because they know it is a lie and they cannot deceive themselves. If that information is non-personal, they deceive themselves into believing that the information they disclose is true," he says.
According to the Professor, this finding is relevant because "working on the discourse, that is, the way in which the economic issue is raised, could condition the answer, reducing the lie."
Under the name 'Personal lies', this project focused on lying and ethical behavior will be completed with a new line of study that is already being conducted, which also addresses the influence of the effort in lying.
More information: Gary Charness et al, Personal lies, Economics Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.econlet.2023.111496
Journal information: Economics Letters
Provided by University of Malaga