This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
The value of information gathering in phage–bacteria warfare
Phages, the viruses that infect bacteria, will pay a high growth-rate cost to access environmental information that can help them choose which lifecycle to pursue, according to a study.
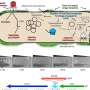
Yigal Meir and colleagues developed a model of a bacteria-phage system to investigate how much the viruses should be willing to invest to acquire information about their local environment. The study is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.
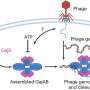
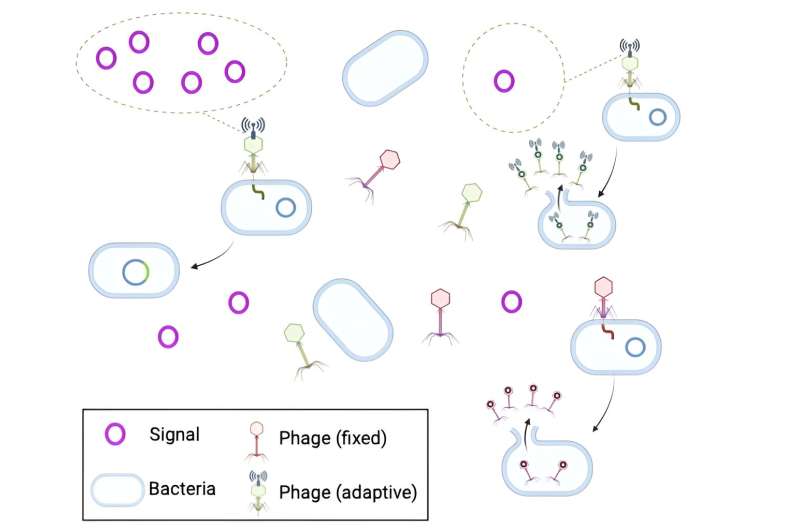
A temperate phage, once inside a bacterium, can choose one of two life cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage turns the bacterium into a factory for additional phages, until the cell is full of phages and the bacterium bursts and dies.
In the lysogenic cycle, the phage inserts its DNA into the bacterial genome. This lysogenic strategy is useful for situations where there are few proximate infection opportunities, either because there are few bacteria nearby or because all nearby bacteria are already infected with related phages.
Once phage DNA is inserted into the bacterium, its progeny will also carry phage DNA, and can produce phages in the future when there are more uninfected targets available. Knowing the extent of infection opportunities can determine which life-cycle would lead to more descendants of the phage in the long run.
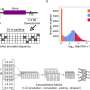
Some phages do have means of sensing the abundance of bacteria nearby, as well as the abundance of phage infection events nearby—but these sensing abilities require genes that come at a cost to the phage. The authors theoretically investigate the "price," in terms of lysogenic growth rate or number of phages released per burst, that phage should be willing to pay to gain environmental information.
According to the authors, a lysogenic phage that has incurred a 50% growth rate penalty to access environmental information will still outcompete a phage that does not sense the abundance of nearby phages or bacteria.
More information: Yuval Dahan et al, The value of information gathering in phage–bacteria warfare, PNAS Nexus (2024). DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad431
Journal information: PNAS Nexus
Provided by PNAS Nexus