This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Scientists find that senescence can accelerate evolution
The mystery of aging has fascinated people for millennia, with many willing to do anything to halt or reverse this process, because aging is typically associated with gradual deterioration of most body functions. While senescence is a natural part of life, biologists understand surprisingly little about the emergence of this process during evolution.
It is not clear whether aging is inevitable because there are organisms that seemingly do not age at all; moreover, the phenomenon known as negative aging, or rejuvenation, does exist: for example, some turtles' vital functions improve with age.
Researchers of the Institute of Evolution led by Academician Eörs Szathmáry have endeavored to prove the validity of a previously proposed but still unproven theory of aging. The theory suggests that under the right circumstances, evolution can favor the proliferation of genes controlling senescence.
The research is published in the journal BMC Biology.
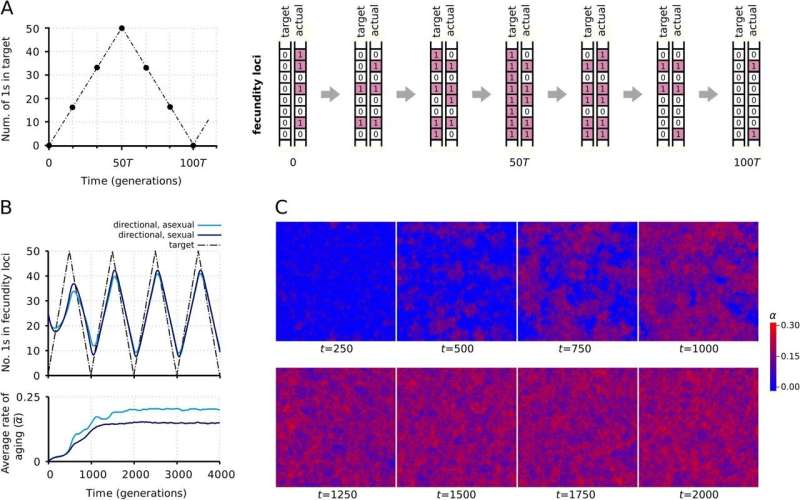
To test the hypothesis, the researchers used a computer model they had developed. This model is an algorithm capable of simulating long-term processes in populations of organisms and genes under circumstances controlled by the scientists. Essentially, with such models, evolutionary scenarios can be run, yielding results in a few hours rather than over millions of years. Modern evolutionary research would be inconceivable without computer modeling.
The fundamental question of the research was simple: Is there any meaning of aging? Does it serve any evolutionary function, or is it indeed a bitter and fatal by-product of life?
"Aging can have an evolutionary function if there is a selection for senescence. In our research, we aimed to uncover this selection," says Szathmáry. "According to classical explanations, aging emerges in the populations even without selection. That is because individuals would die sooner or later without aging as well (as a consequence of illness or accidents), therefore the force of natural selection in the population would get weaker and weaker.
"This creates an opportunity for the genes which have an adverse effect for chronologically old individuals (thus causing senescence) to accumulate. Which would mean aging is only a collateral consequence of evolution and has no adaptive function."
During the last century, using different biological mechanisms, several evolutionary theories were formulated for the explanation of inevitable aging, which has no positive function. Several scientists accepted this assumption as fact, but when non-aging organisms were discovered, more and more researchers questioned the inevitability of senescence, and suggested perhaps aging could have some advantages as well.
"It has become accepted in the evolutionary biology community that the classical non-adaptive theories of aging cannot explain all the aging patterns of nature, which means the explanation of aging has become an open question once again," says Szathmáry.
"Alternative adaptive theories offer solutions for this problem by suggesting positive consequences of senescence. For example, it is possible that in a changing environment, aging and death are more advantageous for individuals, because this way the competition, which hampers the survival and reproduction of the more adaptable progeny with better gene compositions, can be decreased."
However, this scenario holds true only if individuals are predominantly surrounded by their relatives. Otherwise, during sexual reproduction the non-aging individuals "steal" the better (that is better suited for changed environment) genes from the members of the aging population, and therefore the significant senescence disappears.
After running the model, the biologists found that aging can indeed accelerate evolution. This is advantageous in a changing world because the faster adaptation can find adequate traits more quickly, thereby supporting the survival and spread of descendent genes. This means that senescence can become an advantageous characteristic and be favored by natural selection.
More information: András Szilágyi et al, Directional selection coupled with kin selection favors the establishment of senescence, BMC Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12915-023-01716-w
Journal information: BMC Biology
Provided by Ökológiai Kutatóközpont