This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Dryland biocrusts enhance soil carbon release in response to climate warming: Study

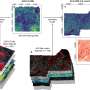
Biocrusts, comprised of diverse organisms such as mosses, lichens, and cyanobacteria, have an enormous influence on soil carbon dynamics. Therefore, understanding the function and response of biocrusts to environmental stressors is essential for ecosystem prediction and management.
A research team led by Prof. Li Xinrong from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found that biocrusts significantly increased soil carbon release, with this effect becoming more pronounced under experimental warming.
The study was published in Soil Biology and Biochemistry on Oct. 20.
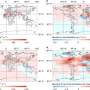
The researchers found that biocrust development in drylands can significantly improve soil carbon release, resulting in an increase in atmospheric CO2 that releases about 66.5 g C m-2yr-1.
Rising temperatures further increase carbon release from biocrust, increasing CO2 efflux by about 22.9 g C m-2yr-1 per °C. This means that biocrust may intensify the carbon cycle between the atmosphere and the soil under climate change, forming positive feedback that further amplifies the effects of climate change.
The researchers found that the increase in net soil exchange (NSE) varied with the type of biocrust and was subject to seasonal fluctuations.
In addition, the researchers observed that biocrusts in drier areas were less sensitive to temperature changes, suggesting an adaptation to warmer conditions.
The variation in NSE associated with biocrusts also suggests potential impacts on the overall fitness of these ecosystems to climate change.
Furthermore, the study highlights the importance of including biocrusts in global carbon models to accurately predict their role under changing environmental conditions.
"These results underscore the complex interaction between biocrusts and their environment, with implications for our understanding of carbon cycling in arid landscapes," said Prof. Li.
More information: Jingyao Sun et al, Biocrusts modulate carbon losses under warming across global drylands: A bayesian meta-analysis, Soil Biology and Biochemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109214
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences