Climate warming will not change greenhouse gas emission of biocrust in arid sandy areas
Climate change marked by global warming is affecting various ecological processes of terrestrial ecosystem.
How greenhouse gas (GHG, including CO2, CH4 and N2O) emissions respond to climate change is directly related to the carbon and nitrogen balance between the atmosphere and terrestrial ecosystem.
Recently, researchers from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have found that climate warming will not change greenhouse gas emission of biocrust in arid sandy areas.
Related results were published in Science of The Total Environment.
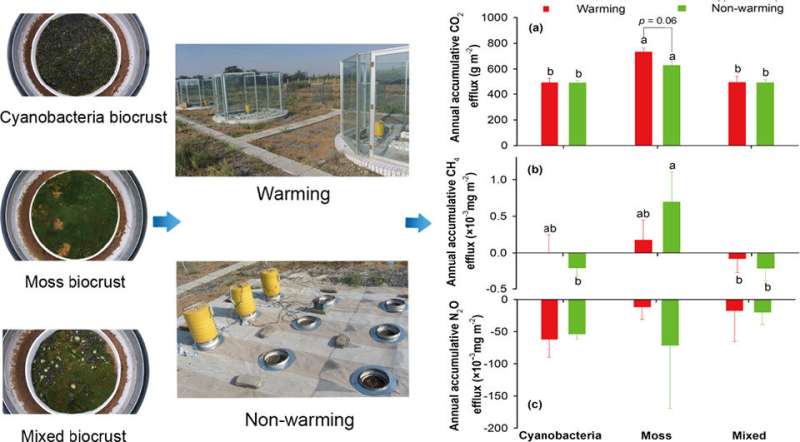
Based on a field warming experiment with open-top-chambers (OTCs) at the Shapotou Desert Research and Experimental Station, the researchers continuously monitored the GHG flux of mosses, algae and their mixture at the annual scale.
They measured CO2, CH4 and N2O effluxes in cyanobacteria-, moss-, and mixed (moss, cyanobacteria and lichen) biocrust soils from 2012 to 2014, covering three growing seasons and two non-growing seasons. The results showed that desert biocrust soils generally acted as a weak sink of atmospheric CH4 and N2O.
Although the effects of global warming on GHG fluxes varied with sampling time and biocrust type, there was no significant difference in daily, monthly and seasonal average CO2, CH4 and N2O effluxes between warming and control in most cases for three biocrust soils.
Besides, the annual cumulative CO2 emissions from moss biocrust warming decreased by 14.2% due to warming, but warming had no significant effect on the other two types of biocrust.
If the drought negative effect caused by warming indirectly and OTC sheltering of precipitation directly was excluded, warming would not significantly change the GHG emissions of biocrust soil ecosystem in arid desert areas.
More information: Yigang Hu et al, Reference for different sensitivities of greenhouse gases effluxes to warming climate among types of desert biological soil crust, Science of The Total Environment (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154805
Journal information: Science of the Total Environment
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences