This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Nano-sized probes reveal how cellular structure responds to pressure
By giving living cells a "nano-poke" and monitoring the resulting changes in the intracellular environment, researchers have gotten their first glimpse of how whole cells respond to external mechanical pressure.
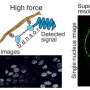
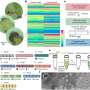
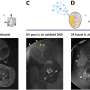
A team led by scientists from the National Institute for Materials Science in Tsukuba, Japan, used a technique called atomic force microscopy to apply force across the surface of various cells. The method uses nanoscale probes, with tips just a few billionths of a meter in size, to measure and map how force gets distributed across the cellular surface and throughout the cell.
The researchers used machine learning to analyze and model the forces they measured. They also used fixing and staining techniques to study how the force distortion affected the cell's internal structures and the microtubules and actin filaments that make up its "skeleton."
The study was published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
"Cells are smart materials that can adapt to various chemical and mechanical stimuli from their surroundings," says Jun Nakanishi, one of the corresponding authors of the study and the leader of the Mechanobiology Group at the National Institute for Materials Science. That ability to adapt relies on rapid feedback mechanisms to keep the cell intact and healthy, and there's growing evidence that the failure of this cellular response underlies a range of ailments, including diabetes, Parkinson's disease, heart attacks, and cancer.
So far, studies of these cellular responses have been limited by the techniques used—for example, some methods require that cells be pre-fitted with sensors, so they can only measure a small part of the response. "We invented a unique way to 'touch' a cell with a nanoscale 'hand,' so that the force distribution over a complete cell could be mapped with nanometer resolution," says Hongxin Wang, who is the first author of the study and JSPS postdoc in the Mechanobiology Group.
The study revealed that tensional and compressional forces are distributed across actin fibers and microtubules within the cell to keep its shape, similar to how the poles and ropes of a camping tent work. When the researchers disabled the force-bearing function of actin fibers, they found that the nucleus itself is also involved in counterbalancing external forces, highlighting the role of the internal structure of the nucleus in the cellular stress response.
The research team also compared the responses of healthy and cancerous cells. Cancer cells proved more resilient to external compression than healthy cells, and they were less likely to activate cell death in response.
The findings not only illuminate the complex intracellular mechanics of the stress response, but the discovery of different responses in cancer cells could offer a new way to distinguish healthy and cancerous cells—a diagnostic tool based on cellular mechanics.
Hospitals currently use the size, shape, and structure of a cell in diagnosing cancer. However, these features don't always provide enough information to tell the difference between healthy and diseased cells.
"Our findings provide another way of checking cell conditions by measuring force distribution, which could dramatically improve diagnostic accuracy," says Han Zhang, another corresponding author of the study and the senior researcher of the Electron Microscopy Group, NIMS.
More information: Hongxin Wang et al, Mapping stress inside living cells by atomic force microscopy in response to environmental stimuli, Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2023.2265434
Journal information: Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Provided by National Institute for Materials Science