This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Building blocks for life could have formed near new stars and planets

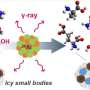
While life on Earth is relatively new, geologically speaking, the ingredients that combined to form it might be much older than once thought. According to research published in ACS Central Science, the simplest amino acid, carbamic acid, could have formed alongside stars or planets within interstellar ices. The findings could be used to train deep space instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope to search for prebiotic molecules in distant, star-forming regions of the universe.
It has long been hypothesized that one of the building blocks for life, amino acids, could have formed during reactions in the "primordial soup" of the early, prebiotic Earth. However, another theory suggests that amino acids could have been carried to the Earth's surface by meteorites.
These space rocks might have picked up the molecules from dust or interstellar ices—water and other gases frozen solid by the cold temperatures of outer space. But because meteorites came from far away in the universe, scientists are left wondering, where did these molecules form, and when?
To help answer these questions, Ralf Kaiser, Agnes Chang and colleagues wanted to investigate the chemical reactions that might have taken place in interstellar ices that once existed near newly forming stars and planets.
The team created model interstellar ices containing ammonia and carbon dioxide, which were deposited onto a silver substrate and slowly heated. Using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, they found that carbamic acid and ammonium carbamate started to form at -348° Fahrenheit and -389° (62 and 39 Kelvin), respectively. These low temperatures demonstrate that these molecules—which can turn into more complex amino acids—could have formed during the earliest, coldest stages of star formation.
In addition, the researchers found that at warmer temperatures, similar to those produced by a newly formed star, two carbamic acid molecules could link together, making a stable gas.
The team hypothesized that these molecules could have been incorporated into the raw materials of solar systems including our own and then delivered to the early Earth by comets or meteorites once the planet formed. They hope this work will inform future studies that use powerful telescopes to look for evidence of prebiotic molecules in the far reaches of space.
More information: Thermal Synthesis of Carbamic Acid and Its Dimer in Interstellar Ices: A Reservoir of Interstellar Amino Acids, ACS Central Science (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c01108
Journal information: ACS Central Science
Provided by American Chemical Society