This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers develop nonlinear optical crystals by unusual cationic substitution strategy
An ideal infrared (IR) nonlinear optical (NLO) crystal must have the advantages of a wide transmittance range, impressive laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT), sufficient birefringence index, bulk single-crystal form, and physicochemical stability.
However, there is often a trade-off between a strong NLO coefficient and a wide band gap toward high LIDT, making it challenging to achieve both properties in a single material.
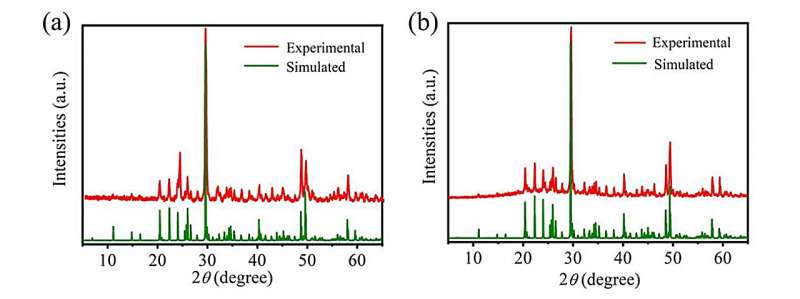
Recently, a research group led by Prof. Guo Guocong from the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported two novel non-centrosymmetric chalcogenides: M[M4Cl][Ga11S20] (M = A/Ba, A = K, Rb) as excellent nonlinear optical crystals.
The study was published in Small on Sept. 11.
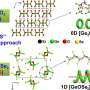
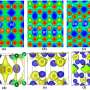
M[M4Cl][Ga11S20] (M = A/Ba, A = K, Rb) represent the first examples achieved by a cationic substitution strategy, resulting in salt-inclusion chalcogenides with diamond-like anionic frameworks.
The researchers used to consider typical diamond-like chalcogenides as promising candidates for IR NLO materials; however, they often exhibit limited LIDTs due to their narrow band gaps.
In this study, the researchers employed an unconventional cationic substitution strategy, [[SZn4]S12 + [S4Zn13]S24 + 11ZnS4 => MS12+ [M4Cl]S24 + 11GaS4], to create two novel salt-inclusion sulfides, M[M4Cl][Ga11S20] (M = A/Ba, A = K, Rb). As anticipated, the introduction of mixed cations in the GaS4 anionic frameworks resulted in wide band gaps (3.04 and 3.01 eV) and improved high LIDTs (9.4 and 10.3 × AgGaS2@1.06 μm).
Furthermore, the researchers found that the ordered arrangement of tetrahedral GaS4 units favored strong second-harmonic generation intensities (0.84 and 0.78 × AgGaS2@2.9 μm).
This study is an example of employing a cationic substitution strategy based on diamond-like structures to create high-performance NLO materials.
More information: Xiao‐Yu Lou et al, Excellent Nonlinear Optical M[M4Cl][Ga11S20] (M = A/Ba, A = K, Rb) Achieved by Unusual Cationic Substitution Strategy, Small (2023). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202305711
Journal information: Small
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences