This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
California supervolcano is cooling off but may still cause quakes
Since the 1980s, researchers have observed significant periods of unrest in a region of California's Eastern Sierra Nevada mountains characterized by swarms of earthquakes as well as the ground inflating and rising by almost half an inch per year during these periods. The activity is concerning because the area, called the Long Valley Caldera, sits atop a massive dormant supervolcano.
Seven hundred sixty thousand years ago, the Long Valley Caldera was formed in a violent eruption that sent 650 cubic kilometers of ash into the air—a volume that could cover the entire Los Angeles area in a layer of sediment 1 kilometer thick.
What is behind the increased activity in the last few decades? Could it be that the area is preparing to erupt again? Or could the uptick in activity actually be a sign that the risk of a massive eruption is decreasing?
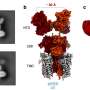
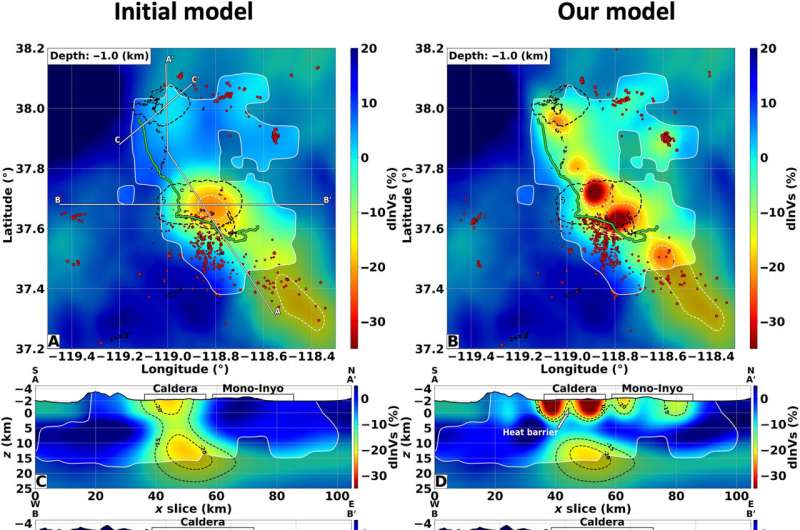
To answer these questions, Caltech researchers have created the most detailed underground images to date of the Long Valley Caldera, reaching depths up to 10 kilometers within the Earth's crust. These high-resolution images reveal the structure of the earth beneath the caldera and show that the recent seismic activity is a result of fluids and gases being released as the area cools off and settles down.
The work was conducted in the laboratory of Zhongwen Zhan, professor of geophysics. A paper describing the research appears in the journal Science Advances on October 18.
"We don't think the region is gearing up for another supervolcanic eruption, but the cooling process may release enough gas and liquid to cause earthquakes and small eruptions," says Zhan. "For example, in May 1980, there were four magnitude 6 earthquakes in the region alone."
The high-resolution image shows that the volcano's magma chamber is covered by a hardened lid of crystallized rock, formed as the liquid magma cools down and solidifies.
To create underground images, the researchers infer what the subsurface environment looks like by measuring seismic waves from earthquakes. Earthquakes generate of two types of seismic waves: primary (P-waves) and secondary (S-waves). Both kinds of waves travel at different speeds through different materials—waves are slowed down by elastic materials like liquids but travel quickly through very rigid materials like rock.
Using seismometers at various locations allows one to measure discrepancies in the timing of the waves and determine the characteristics of the materials—how elastic or rigid—they traveled through. In this way, researchers can create images of the subsurface environment.
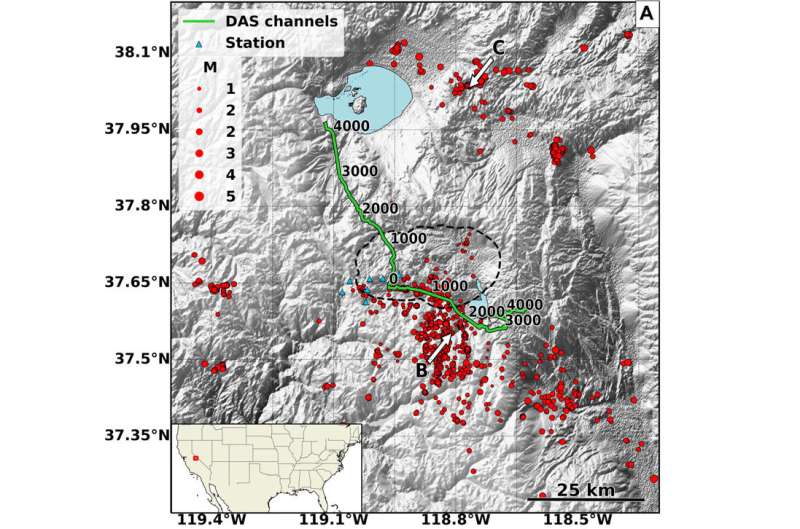
Though there are several dozen seismometers placed throughout the Eastern Sierra region, Zhan's technique utilizes fiber optic cables (like those that provide internet) to make seismic measurements in a process called distributed acoustic sensing (DAS).
The 100-kilometer stretch of cable used to image the Long Valley Caldera was comparable to a stretch of 10,000 single-component seismometers. Over a year and a half, the team used the cable to measure more than 2,000 seismic events, most too small to be felt by people. A machine learning algorithm processed those measurements and developed the resulting image.
This study is the first time that such deep, high-resolution images have been created with DAS. Previous images from local tomography studies have either been confined only to the shallow subsurface environment at depths of about 5 kilometers, or covered a larger area in lower resolution.
"This is one of the first demonstrations of how DAS can change our understanding of crustal dynamics," says Ettore Biondi, DAS scientist at Caltech and the paper's first author. "We're excited to apply similar technology to other regions where we are curious about the subsurface environment."
Next, the team plans to use a 200-kilometer length of cable to image even deeper into the Earth's crust, to around 15 to 20 kilometers deep, where the caldera's magma chamber—its "beating heart"—is cooling.
In addition to Biondi and Zhan, co-authors are former Caltech postdoctoral fellow Weiqiang Zhu, now of UC Berkeley; Caltech postdoctoral scholar Jiaxuan Li; and former Caltech graduate student Ethan Williams, Ph.D., now of the University of Washington.
More information: Ettore Biondi et al, An upper-crust lid over the Long Valley magma chamber, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi9878
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by California Institute of Technology