This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New post-translational modification of the glycolytic enzyme enolase
Proteins are subject to post-translational chemical modifications that result in functional diversity. Methylation is one such modification that is generally believed to occur on lysine and arginine residues. Recently, this modification has been shown to occur on histidine residues as well.
In addition, it has been suggested that histidine methylation occurs in a wide range of proteins. However, many details remain unknown: for example, which are the proteins that are methylated and modified and which are the histidine residues in cells, tissues, or organs where such modifications occur are not known.
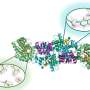
Using mouse skeletal muscle and brain tissue and using a combination of methods based on biochemical protein fractionation and analytical chemistry, a research group from the University of Tsukuba identified γ-enolase, a subunit of the glycolytic enzyme enolase, as a new substrate for the methylation of histidine residues. The work is published in The Journal of Biochemistry.
Among the three amino acid sequences of enolase (i.e., α, β, and γ), the 190th histidine residue of γ-enolase, which is specifically expressed in the central nervous system was found to be methylated.
A conformational prediction study suggested that the histidine residue that undergoes methylation in γ-enolase may be important for intermolecular hydrogen bonding during subunit dimer formation. It was found that the disruption of hydrogen bonding at this site of γ-enolase by substituting histidine with another residue resulted in the suppression of the subunit dimerization and enolase activity. None of the three histidine methyltransferases previously identified in mammals catalyzed the methylation reaction of γ-enolase.
From these results, the newly identified γ-enolase is expected to be a unique research tool for exploring new histidine methyltransferases.
More information: Fumiya Kasai et al, γ-enolase (ENO2) is methylated at the Nτ position of His-190 among enolase isozymes, The Journal of Biochemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvad042
Provided by University of Tsukuba