This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Euroskeptics more likely to think of the EU as less democratic than it is, study shows
A significant share of voters see the EU as less democratic than it really is and believe the European Commission can steamroll its member states, a new study shows.
The research shows that key channels of legitimation in the EU are not well known by the citizens of large member states. Whether people see themselves only as citizens of their nation, or simultaneously as a European, is linked to what they believe about the EU.
A substantial share of EU voters who took part in the study believed that the members of the European Parliament are not directly elected. Many assumed the European Parliament is unimportant for decision making in Brussels.
Less than half of those who took part in the research knew which powers the EU has and which it does not have.
Some were aware of their gaps in knowledge about EU institutions, but a large number who had gaps in their knowledge also thought they were informed.
Those who said they did not hold a European identity were more likely to assume that the EU is less democratic than it is.
The research, published in the journal European Union Politics, was carried out by Florian Stoeckel, Jack Thompson and Jason Reifler from the University of Exeter, Vittorio Mérola from Durham University and Benjamin Lyons from the University of Utah.
Professor Stoeckel said, "Not knowing how a complex institution like the EU works is completely understandable but it is problematic when people have the wrong idea about how the institution works and assume the organization is not as democratic as it is or has power over member states that it doesn't have. Populist parties can mobilize or exploit such misperceptions, or they create them in the first place."
"Our findings help elucidate the rhetorical value of 'taking back control' from Brussels. Indeed, to voters who believe that the European Commission can legislate against the will of a majority of MEPs or member states, European integration is likely to appear like an absolute loss of the sovereignty of the general will, rather than just a transfer of authority to another level."
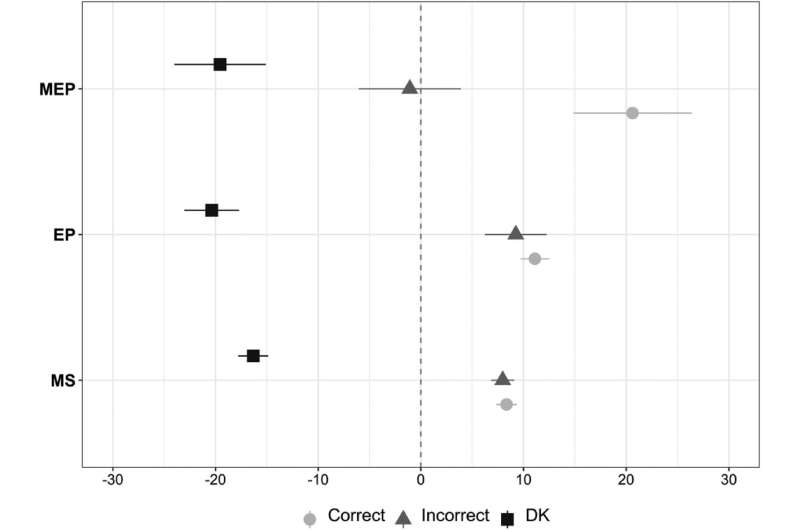
Researchers carried out a survey in France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, and Sweden, with approximately 1,000 respondents per country, in February 2019. Participants were asked three questions—if MEPs are directly elected by voters; to react to the following statement: 'the European Commission can issue new laws even when a majority of MPs of the European Parliament objects' and whether the following statement is correct: 'the European Commission can issue new laws for the EU even when a majority of member states objects."
While the exact proportions vary by country and issue, the combined share of the uninformed and misinformed made up more than half of respondents.
For instance, a third (35 percent) of respondents knew the European Commission cannot pass laws against the will of a majority of Member States. In contrast, 40 percent of respondents wrongly believed the EC could override the will of member states, while another 25 percent were uninformed.
Respondents who took part in the study who described their identity in a narrow, national way thought of the EU as an organization with more unrestricted powers. They are more likely to wrongly believe MEPs are not directly elected and the European Commission can rule over the European Parliament and EU member states. They were less likely to know legislation needs to be approved by a majority of MEPs in order for it to become law.
Substantial portions of the public in all six countries were either uninformed or misinformed. Pooling responses across countries showed 19 percent held the misperception that MEPs are not directly elected and 21 percent of respondents answered that they 'don't know.'
A total of 22 percent of respondents said the European Commission could pass laws while overriding the objection of the European Parliament, while 27 percent of the respondents selected the 'don't know' category.
Only 35 percent of respondents correctly said that the European Commission cannot pass laws against the will of the member states of the EU, whereas 40 percent of respondents held a misperception and another 25 percent of respondents chose 'don't know.'
More information: Florian Stoeckel et al, Public perceptions and misperceptions of political authority in the European Union, European Union Politics (2023). DOI: 10.1177/14651165231193833
Provided by University of Exeter



















