This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers develop stepwise strategy for carbon dioxide reduction to multicarbon products
Though efficient C2+ production from CO2 electrocatalytic reduction reaction (CO2ERR) has become a promising approach to mitigate CO2 emissions and store intermittent renewable energy, it suffers from low selectivity and undesired side reactions.
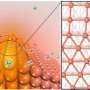
Recent studies have shown that serial hollow-fiber penetration electrodes (HPEs) can improve the CO2ERR performance by forcing CO2 to disperse and penetrate through the abundant pores on HPE wall, which boosts CO2ERR kinetics.
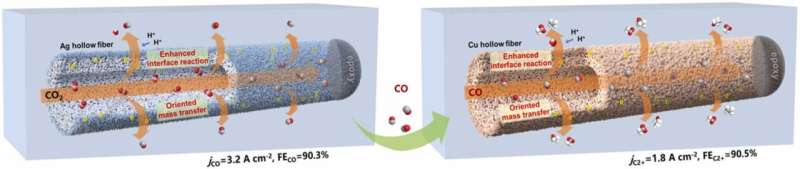
To promote the selectivity and current density for C2+ products simultaneously, a research team led by Profs. Chen Wei and Wei Wei from the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a stepwise CO2ERR strategy using Ag and Cu HPEs to reach high-rate C2+ production.
The results were published in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.
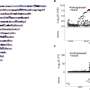
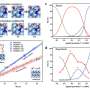
In the stepwise CO2 electroreduction, CO2 was firstly reduced into CO over chloride ion-regulated Ag hollow-fiber penetration electrodes with a 3.2 A cm-2 partial current density and a 90.3% faradaic efficiency of CO. Then, the chloride ion-regulated Cu hollow-fiber penetration further converted CO into C2+ products with 1.8 A cm-2 partial current density and 90.5% faradaic efficiency of C2+ products. Both steps were steadily conducted under total current density of 2 A cm-2 for 200 hours.
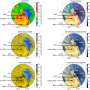
Experimental results and density functional theory calculations showed that synergetic combination of the unique penetration effect and the regulated electronic structures resulted in the superior performance toward C2+ production.
This work sheds light on designing electrocatalytic systems with exceedingly efficient CO2 electroreduction of high current density and selectivity as well as good durability, which might contribute to the scalable CO2 electroreduction applications towards high-value C2+ chemicals.
More information: Xiao Dong et al, Highly efficient ampere-level CO2 reduction to multicarbon products via stepwise hollow-fiber penetration electrodes, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122929
Journal information: Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences